Authentication and Authorization are often used interchangeably but they are distinct security processes in identity and access management (IAM).
Authentication is the process of verifying your identity by confirming your credentials, such as your username/user ID and password. The system then uses your credentials to verify that you are who you claim you are.
Authorization is the process of determining whether an authenticated user has access to specific resources. After the system has properly confirmed your identity, you will be granted complete access to resources such as information, files, databases, finances, and so on.
The key difference between authentication and authorization is that the user or service identity is confirmed through authentication, and their access privileges are established through authorization.
What is Authentication?
Authentication is a process that identifies the identity of an oncoming user. This is the root step of all Identity Management. Identification of identity is simple – a set of credentials are accepted by a user and he/she is authenticated if those credentials are correct.
Sometimes, there can be another layer to this authentication, and the user might need to pass through a more complex but secure authentication process than just simple credentials passing. A user’s identity is verified by many different factors through this process before the system grants them access to anything. This may include a time-bound OTP, a set of questions, a hardware token, biometrics, etc.
What is the Purpose of Authentication?
The main purpose of authentication is to verify and validate the identity of an individual or entity trying to access a system, application, or resource. It ensures that the user is who they claim to be and grants them appropriate access privileges based on their authenticated identity. This ensures that unauthorized personnel or impostors cannot illegally get access to critical resources.
Authentication serves as a fundamental security measure to protect sensitive information, prevent unauthorized access, and maintain the integrity and confidentiality of data. It plays a crucial role in establishing trust, mitigating security risks, and safeguarding user accounts and resources from unauthorized use or malicious activities. Authentication is a very pivotal part of Identity and Access Management for modern organizations.
What are the Popular Authentication Methods?
Over the years, a wide range of authentication methods have been developed. Now, we’ll go through the most popular forms of authentication and demonstrate how each method works in modern systems.
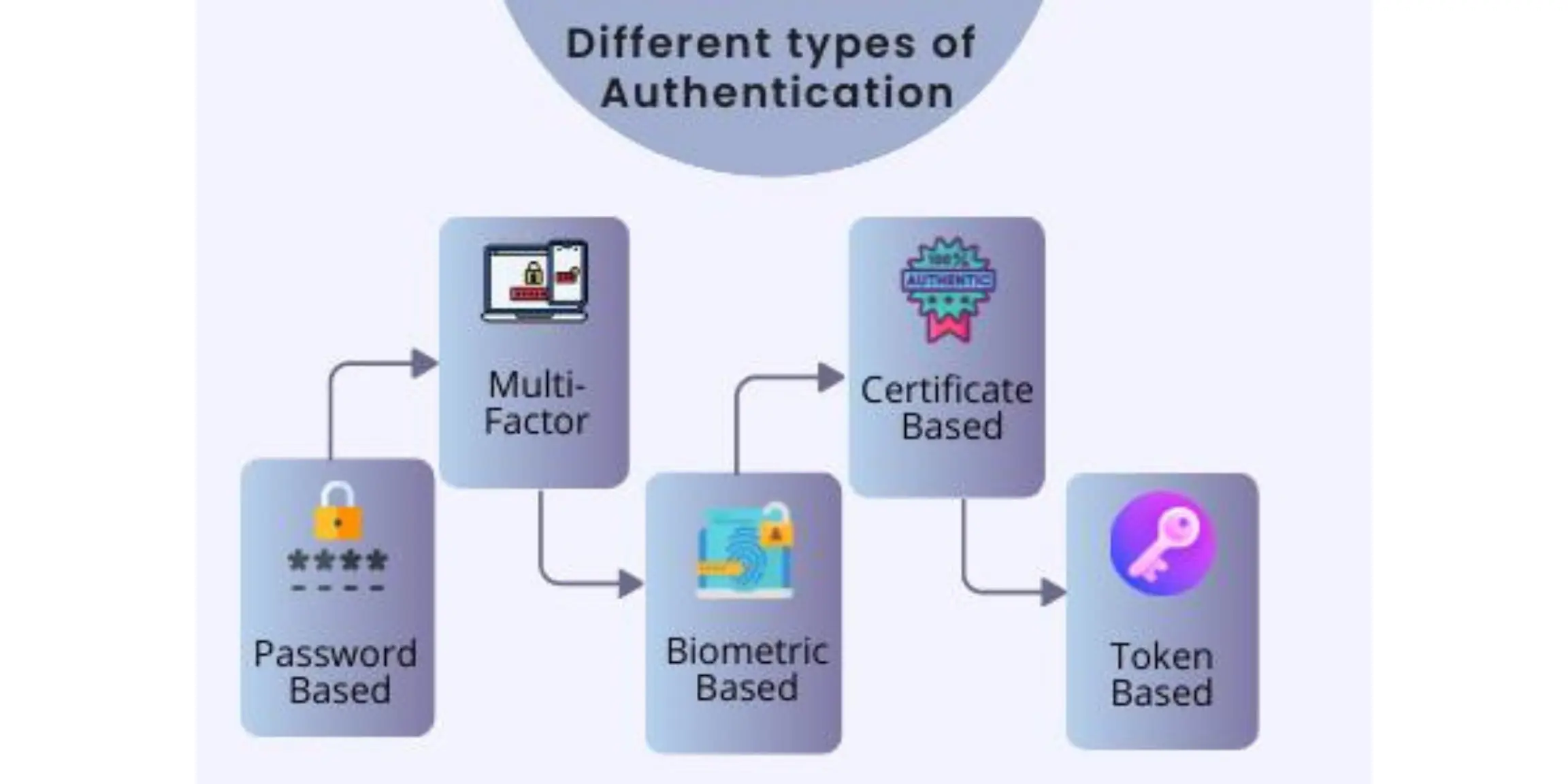
Biometric:
Biometric authentication is a method of verifying a person’s identity using their unique biological traits. It assists you in verifying individuals and ensuring that they are who they say they are. The biometric data of the users is collected and stored in a database, which is later compared to ensure that the user is authenticated. Different types of biometric authentication include fingerprint scanners, eye scanners, voice recognition, face identifier, etc.
Password-based:
The most frequent way of authentication is passwords. A string of letters, numbers, or special characters can be used as a password. You must develop strong passwords that incorporate a mix of all possible solutions in order to secure your identity.
Single Sign-On Authentication:
This method of authentication enables users to access different applications, resources, and systems using a single set of credentials. Single Sign-On streamlines the authentication process, which provides a seamless user authentication experience. It improves productivity and security at the same time.
Multi-factor:
Multi-Factor Authentication is the most advanced mechanism, requiring two or more levels of protection from multiple authentication categories to enable user access to the system. To prevent security breaches, this includes elements that are independent of one another.
Passwordless Authentication:
In passwordless authentication users do not need passwords to authenticate, instead, other methods like OTP, Email Verification, Biometrics, etc., are used for authenticating the user identity. This method eliminates password management hassles and password-theft risks.
API:
The process of confirming a user’s identity while requesting to access server-side services is known as API authentication. Basic HTTP, core API, and 0Auth are only a few of the most used APIs.
Certificate-based:
Digital certificates are used in certificate-based authentication solutions to identify individuals, computers, and devices. A digital certificate is a type of electronic document similar to a driver’s license or passport. Only a certification authority may issue digital certificates to show ownership of a public key.
What is Authorization?
Authorization is the process that determines what level of access a user will get to critical resources of the organization. Authorization deals with the role of an individual within an organization or a group. Considering an example, the employee who belongs to the Accounts and Finance team will be authorized to only Account-related tools and applications, and not the Sales and Business-related tools.
Authorization of a user is very important, as most web resources today are to be selectively shared among user bases, and most online business models also run this way. That is the reason why it is one of the most crucial steps when talking about access management.
What are the Popular Types of Authorization?
Below are some of the techniques used for the authorization process. Each of these techniques works differently and is important in its own way to secure data.
API Keys:
The API key is a long string that is usually provided in the URL or header of the request. The API key is mostly used to identify the individual initiating the API request (authenticating you to use the API). Most APIs require you to sign up for an API key before you can use them.
Open ID:
The Open ID layer is an authorization authentication layer built on top of the 0auth2.0 framework. It enables clients to validate the end user’s identification using the authorization server and to acquire basic profile information about the end user in an interoperable and REST-like manner.
SAML:
SAML is an XML-based authentication and authorization mechanism that connects two entities: the SP and the IDP. Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is a standard SSO in which verified data is transferred via digitally signed XML documents.
HMAC: Hash-based Message Authentication Code is a digital signature technique that makes use of message digest algorithms like MD5 and SHA-1 to produce a reliable data integrity protocol.
HTTP:
Authentication and authorization both employ this mechanism. To establish their identity, a user typically submits a username and password. This technique excludes cookies, session IDs, and login pages since the HTTP header is used.
While considering Authentication and Authorization, Authorization can only be granted after Authentication.
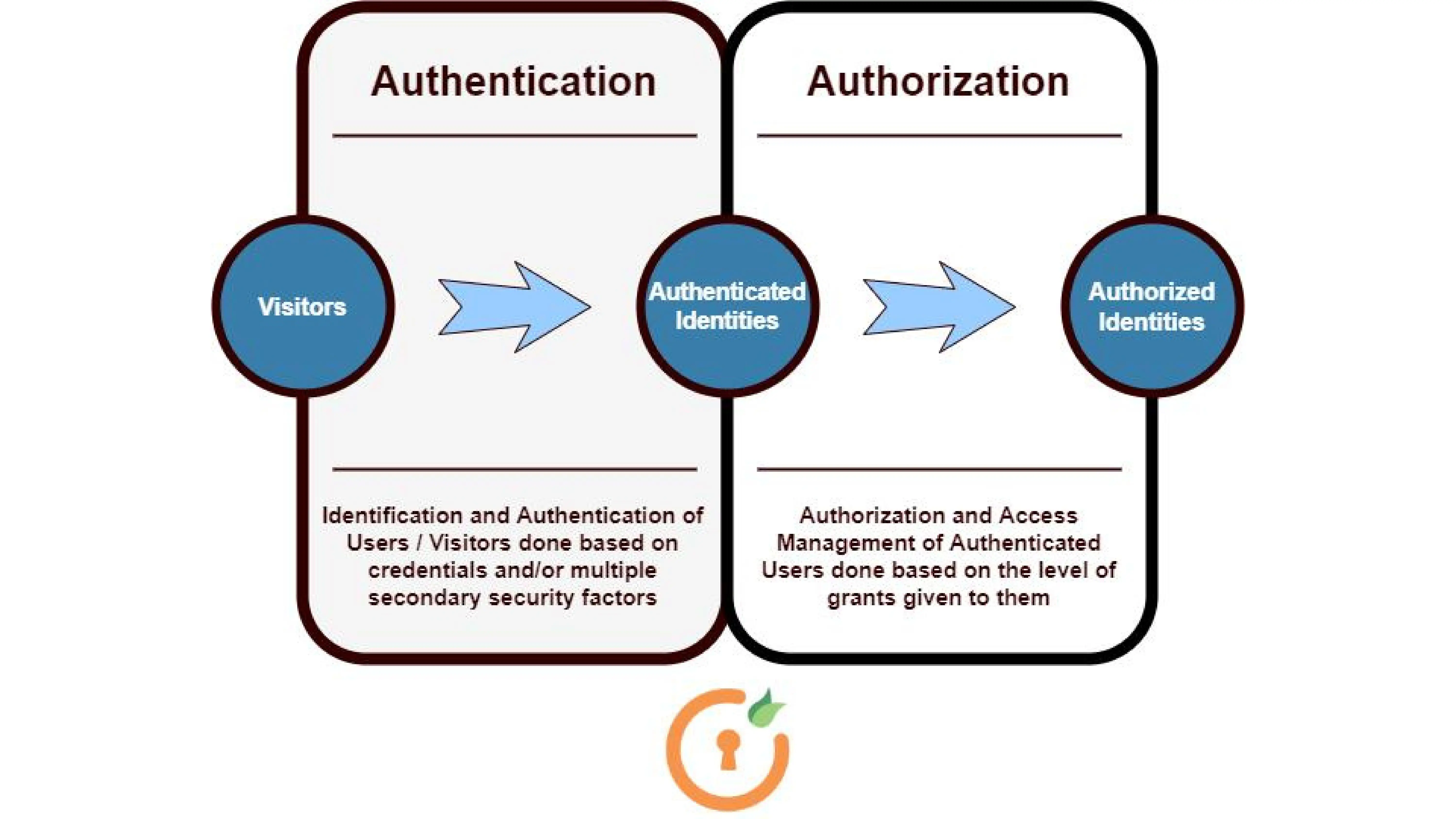
Authentication VS Authorization {authentication-vs-authorization}
| Authentication | Authorization |
|---|---|
| Authentication is the process of verifying who a user is through Login or Passwords. | Authorization gives those users permission to access a resource. |
| It works through passwords, biometrics, and other information provided or entered by the user. | Authorization works through settings that are implemented and maintained by the organization. |
| It is visible & partially changeable by the user. | Authorization isn’t visible & changeable by the user. |
| Data is transferred through ID Tokens (JWT Token). | Data transmits through Access Tokens. |
| Authentication is usually done before Authorization. | Authorization can only be granted after Authentication. |
| e.g. When a college student walks into their campus, they have to showcase their identity card at the gate to get authenticated as a student of the institution. | e.g. Once the student is authenticated they walk towards their pre-allocated building, towards their floor, and their classroom. This is where Authorization is in play, the student does not have access to the professor’s cabin or the principal’s office. |
Authentication and Authorization in Cloud Computing
Authentication and authorization are essential components required for securing cloud computing environments. They help ensure that only authorized individuals or entities can access resources and perform actions within the cloud infrastructure.
Different Authentication methods discussed in this article can be implemented to verify the identity of a user or entity requesting access to a system or resource within the cloud. Different authentication mechanisms are used to establish trust between the user and the cloud service provider (CSP).
In cloud computing, Authorization or access control is used for granting or denying permissions to authenticated users based on their roles, responsibilities, or other attributes within the cloud environment. Authorization mechanisms help enforce the principle of least privilege, ensuring that users only have access to the resources they need.
How miniOrange can help you Implement Authentication & Authorization in your Organization?
Being in a high-paced cyber world, it’s an important need for enterprises to adopt Authentication and Authorization mechanisms to fortify their security posture. To successfully implement these robust security measures in your organization, you need a customized Identity and Access Management (IAM) solution from a trusted IAM vendor.
miniOrange provides a wide array of solutions that efficiently and securely enable Identity and Access Management for your organization in On-Premise, Cloud, and Hybrid environments. But before choosing any cloud Security Service provider for implementing Authentication and Authorization mechanisms, you should confirm they confidentially handle your information, with the simplest technical support at a budgeted price. The miniOrange IAM solution is highly customizable, scalable, and fits your organization’s unique needs. You can leverage the miniOrange Free Trial to try out our IAM solution & test all the features to make better and more well-informed decisions.
FAQ
Which comes First, Authentication or Authorization?
In the Identity and Access Management process, authentication typically comes before authorization. Authentication is the process of verifying digital identities. Once authenticated, the next step is authorization. Authorization determines what actions and resources a user is allowed to access.
Further Reading:
Author




Leave a Comment