Consider an organization utilizing various platforms for communication, collaboration, cloud services, and financial management, with each user possessing different credentials for each application.
Speaking of security breaches, a 2022 study revealed that 84% of organizations have fallen victim to at least one identity-related breach in the previous year due to weak identity management. This is where Centralized Identity Management comes in as a savior.
Centralized Identity Management addresses the aforementioned challenges by unifying user credentials across all platforms, streamlining access, and enhancing security.
In this write-up, we will look into the nuances of centralized identity management (CIM), how it works, and its importance while shedding light on decentralized identity management. So, let’s begin with understanding what centralized identity management is.
What is Centralized Identity Management?
Centralized Identity Management (CIM) is a system that consolidates the management of users' digital identities and access permissions across multiple applications, platforms, and services. Instead of managing identities separately for each system, CIM centralizes control, providing a single source of truth for user authentication, authorization, and access rights.
Key Functions of Centralized Identity Management:{#key-functions-of-centralized-identity-management}
Authentication: Verifies user identities using credentials like usernames, passwords, or multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Authorization: Determines what resources a user is allowed to access based on their roles and permissions.
Provisioning: Automates the process of creating, updating, and removing user accounts across connected systems.
Auditing: Tracks user activity and access for compliance and security.
Before we head into the details of CIM, let's understand how Centralized Identity Management Works.
How does Centralized Identity Management Work?
Centralized Identity Management (CIM) works by unifying the control of user identities, authentication, and access permissions across multiple systems and applications under a single platform or directory. This centralized approach streamlines the process of managing user credentials, permissions, and access policies, ensuring security, efficiency, and scalability for organizations.

Central Directory: The centralized Identity Management (CIM's) core is a central repository, like Active Directory (AD) or a cloud-based directory service. This repository serves as the single source of truth for all user identities, storing information such as usernames, passwords, roles, and access permissions.
User Authentication: When a user attempts to log in to an application or service, the Centralized Identity Management system authenticates the user's credentials against the central directory.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): CIM assigns roles to users based on their position or department within the organization. These roles define what resources and services the user can access. The roles and permissions are centrally managed, ensuring consistency and compliance with security policies.
Provisioning and De-provisioning: As users join or leave the organization, the CIM system automates the provisioning or de-provisioning of their accounts. New employees are automatically granted the necessary access to tools based on their role, and when employees leave, their access is revoked across all connected applications, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Auditing and Reporting: A key aspect of CIM is its ability to track user activities, including login attempts, resource access, and permission changes. These logs are stored centrally, providing visibility for compliance audits and helping detect potential security breaches.
By unifying identity management, CIM enhances security, improves operational efficiency, and ensures that organizations maintain compliance with data protection standards.
Challenges of Centralized Identity Management
Although Centralized Identity Management offers streamlined user authentication and access control, it also comes with certain challenges. Let’s look into them in detail.
Single Point of Failure: A centralized system can become a single point of failure. If compromised, it may expose an entire organization's identity infrastructure to cyberattacks.
Scalability Issues: As an organization grows, managing identities from multiple devices, locations, and applications can strain the centralized system, making scalability a concern.
Security Vulnerabilities: Concentrating identity data in one place makes it a prime target for cybercriminals. A large volume of sensitive data could be exposed if the system is breached.
Integration Complexity: Organizations often use diverse applications and systems. Ensuring seamless integration with all of them is complex, especially with legacy systems or third-party applications.
Privacy and Compliance: Storing personal identity data centrally must comply with data privacy regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. Ensuring compliance across regions can be difficult.
Access Control Challenges: Defining, enforcing, and auditing access policies consistently across various departments, devices, and users requires careful planning and sophisticated tools.
Looking at these challenges, one may think what could be the alternative to centralized identity and access management? Well, this is where we talk about decentralized identity management.
What is Decentralized Identity Management?
Decentralized Identity Management (DIM) is an approach to identity management where control over digital identities is shifted from a central authority to individuals or distributed systems. Instead of relying on a single organization to manage and verify identities (as in centralized systems), decentralized identity frameworks enable users to create and manage their own identities, often using blockchain or other distributed technologies.
To determine whether centralized or decentralized account management is better for preventing cybercrime and optimizing provisioning workflows, it's essential to explore the differences between the two identity management models. Each approach offers distinct advantages in terms of security and efficiency, and understanding these can guide the decision-making process. Let's delve into the key differences between centralized and decentralized identity management.
Centralized Vs. Decentralized Identity Management
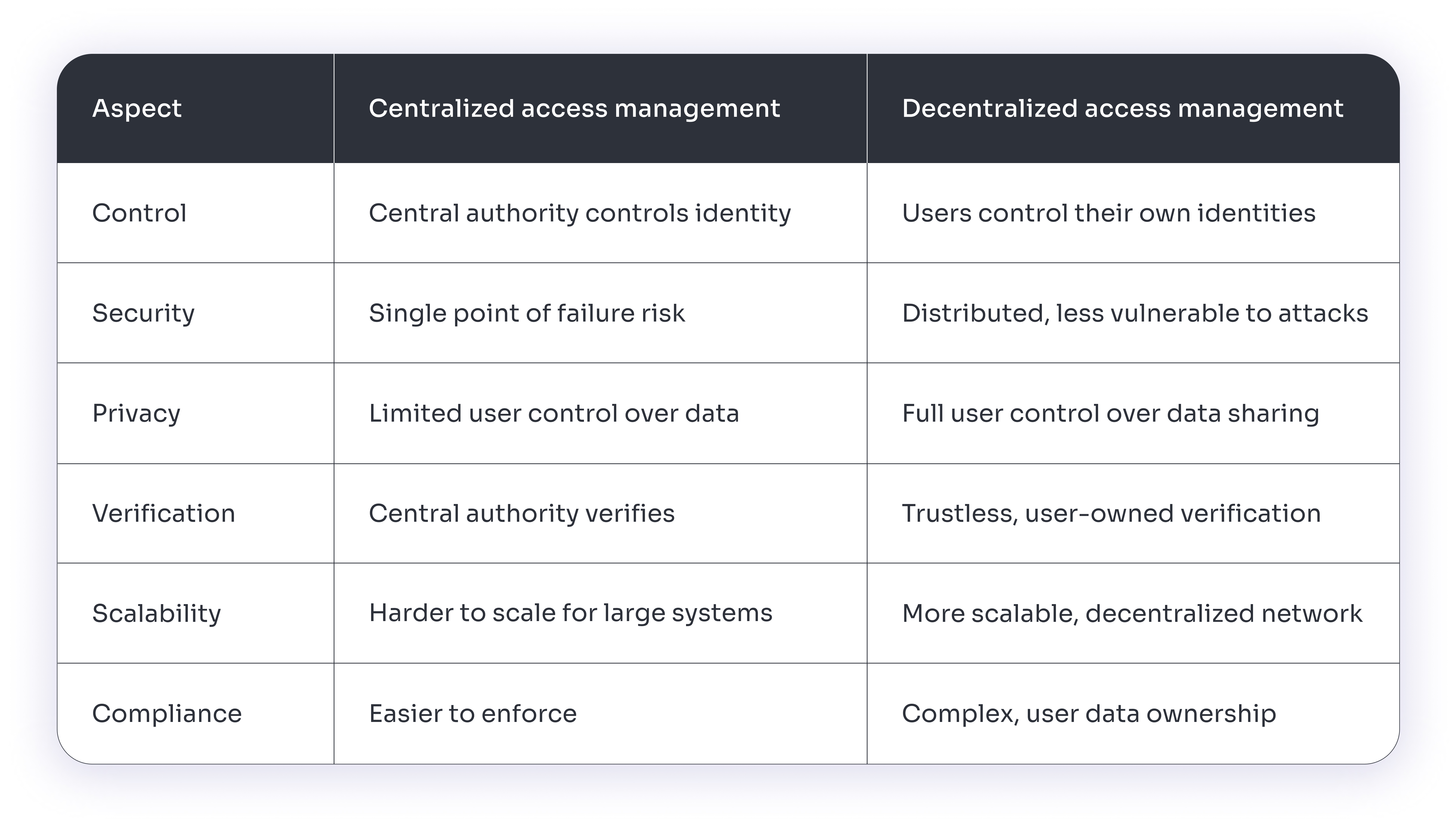
The primary difference between centralized and decentralized identity management lies in how identities are managed, controlled, and verified. Here's a detailed breakdown of the key distinctions:
| Aspect | Centralized Identity Management | Decentralized Identity Management |
|---|---|---|
| Control and Ownership | Control over identity data is with a single authority or organization as users' credentials and personal data are stored in a centralized database managed by the organization. The organization makes decisions about access, policies, and identity usage | Control over identity data is distributed, and users themselves own and manage their own digital identities. Instead of being stored in a single database, identity credentials may reside with the individual or across multiple nodes in a decentralized network. Here, the users decide how, when, and with whom they share their identity information. |
| Security | Security breaches can be severe, affecting all users in the centralized system as it is more prone to a single point of failure—if the central system is compromised. | Security is enhanced by distributing control across multiple points, minimizing the risk of a single breach. The lack of a central repository means attacks are harder to execute on a large scale, making the system more resilient. |
| Privacy | Privacy is often a concern because all user identity information is stored centrally. The organization controlling the data may collect, analyze, or share personal information without the user's full knowledge or consent. | Users have full control over their identity data and can choose which information to share with third parties, maintaining greater privacy. Systems are often built with privacy by design, ensuring that minimal personal data is shared. |
| Verification Process | The central authority handles verification. The organization managing the system is responsible for authenticating users and granting access to resources. Trust is placed in the central authority to manage and secure user credentials properly. | Verification is done through self-sovereign identities or cryptographic proof. Users present verifiable credentials issued by trusted parties, but the central authority is not needed for every authentication. Trust is distributed across a network, using blockchain or similar technologies to verify the authenticity of credentials without a central authority. |
| Scalability | As the number of users, devices, and applications grows, the system can become harder to scale and manage. Centralized systems may struggle with bottlenecks, especially as they expand across regions or need to integrate with multiple applications. | Decentralized systems are inherently more scalable because they do not rely on a single point of control. They can expand without a corresponding increase in complexity or bottlenecks. They are designed to support widespread interoperability across different platforms and networks. |
| Compliance and Governance | Easier for organizations to govern and enforce policies since they control all user data and can ensure compliance with legal regulations. However, centralized systems must comply with stringent data privacy regulations like GDPR, which can add complexity to managing sensitive data. | Compliance becomes more complex, as users own their data and the organization does not directly manage personal information. However, decentralized systems may reduce exposure to legal risk since the organization does not store large amounts of personal data. |
Let’s Summarise It:
Centralized or Decentralized: Which One is Better?
For Organizations Needing Full Control: Centralized systems are often more suitable for organizations that need efficient control over user identities and simplified management, especially for enterprises with existing centralized infrastructures.
For Privacy-Conscious or Highly Secure Environments: Decentralized systems are ideal for organizations or sectors (like finance or healthcare) that prioritize user privacy, security, and data protection. They are particularly effective when users need to manage their own identity across multiple services.
Hybrid Approach: Many organizations are opting for a hybrid approach, where centralized systems are used for certain services and decentralized elements are adopted for specific privacy-focused use cases. This allows for a balance of control, security, and user privacy.
In short, centralized identity management works well for organizations needing control, simplicity, and integration, while decentralized identity management is better for users seeking privacy, security, and self-sovereignty over their identity. The choice depends on an organization’s priorities, scale, and the type of system best suited for their users or customers.
Increasing Demand for Identity and Access Management
In conclusion, as organizations continue to face security challenges and regulatory demands, the need for effective Identity and Access Management (IAM) systems is paramount. In fact, as per reports, the IAM market size is expected to record a compound growth rate of 14.5% between 2020 and 2025.
Whether through centralized or decentralized identity management, the goal remains the same: to protect user data, streamline access control, and ensure compliance. While both approaches have their strengths, the right solution depends on an organization's specific needs, priorities, and infrastructure.
At miniOrange, we specialize in providing comprehensive IAM solutions tailored to meet the unique demands of businesses across industries. Our solutions streamline centralized identity management, ensuring security, scalability, and seamless integration with existing systems. Whether you're looking for robust role-based access control, user authentication, or identity provisioning, miniOrange has the expertise and tools to help safeguard your organization against identity-related threats while improving operational efficiency.
Discover how miniOrange's IAM solutions can transform your identity management strategy and secure your business today.
Author




Leave a Comment