With the increasing stats and power of cybercrimes, continuous development of the latest authentication schemes is necessary to tackle the rising cyber threats. Custom Database – also sometimes referred to as – Database as Authentication Source is one such authentication method that’s gaining popularity, thanks to the benefits it offers. Let’s take a glance at what it is, how it works, its pros and cons, and why it is gaining popularity.
What is a Custom Database Connection?
A Custom Database Connection is essentially linking your Database or User store with any Identity Platform for user authentication. With this connection, you create an interface between a Database and the Identity Provider, which lets the Database act as an Identity Provider for user authentication. Here you would possibly be thinking of migrating your users from Database (MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc) to the IDP, but that’s not always the safest option. However, with miniOrange, you don’t have to move user Identities from your existing Database to the IDP. The database connection is handled by API endpoints which helps in providing authentication services without migrating your sensitive user identities.
In most cases Custom Database is employed by Organizations for the following purposes:
To Authenticate: Integrate Database as IDP (Identity Provider) to authenticate users.
To Migrate: To migrate your users from existing databases/ user stores for authentication processes.
Database Authentication by miniOrange is handled by 2 specific features:
- Auto-Sync users with existing Database
- Without migrating your users
Auto-Sync users with existing Database
In the following use-case, whenever a user tries to log in for the first time a new record is made within the miniOrange platform, without storing the user password. Here on, miniOrange auto-syncs a new user identity to your local custom database to take care of user tracking for further authentication. You don’t have to make any additional effort to move new user identities from the miniOrange IDP to the Database whenever a user logs in.
For all future authentication of users, miniOrange will always use the existing database/identity store and the respective identity it contains while authenticating the user.
Without migrating your users
In this use case, whenever a new user logs in for the first time, miniOrange automatically creates the user Identity in an identity source which is handled by miniOrange. But before authenticating the user, miniOrange ensures the user must be successfully authenticated against the legacy identity store (Your own Database), and only then the user profile is going to be created in the miniOrange Identity Platform. The new users are going to be created using an equivalent id and password that was provided by the user during authentication.
How does Custom Database Connection work?
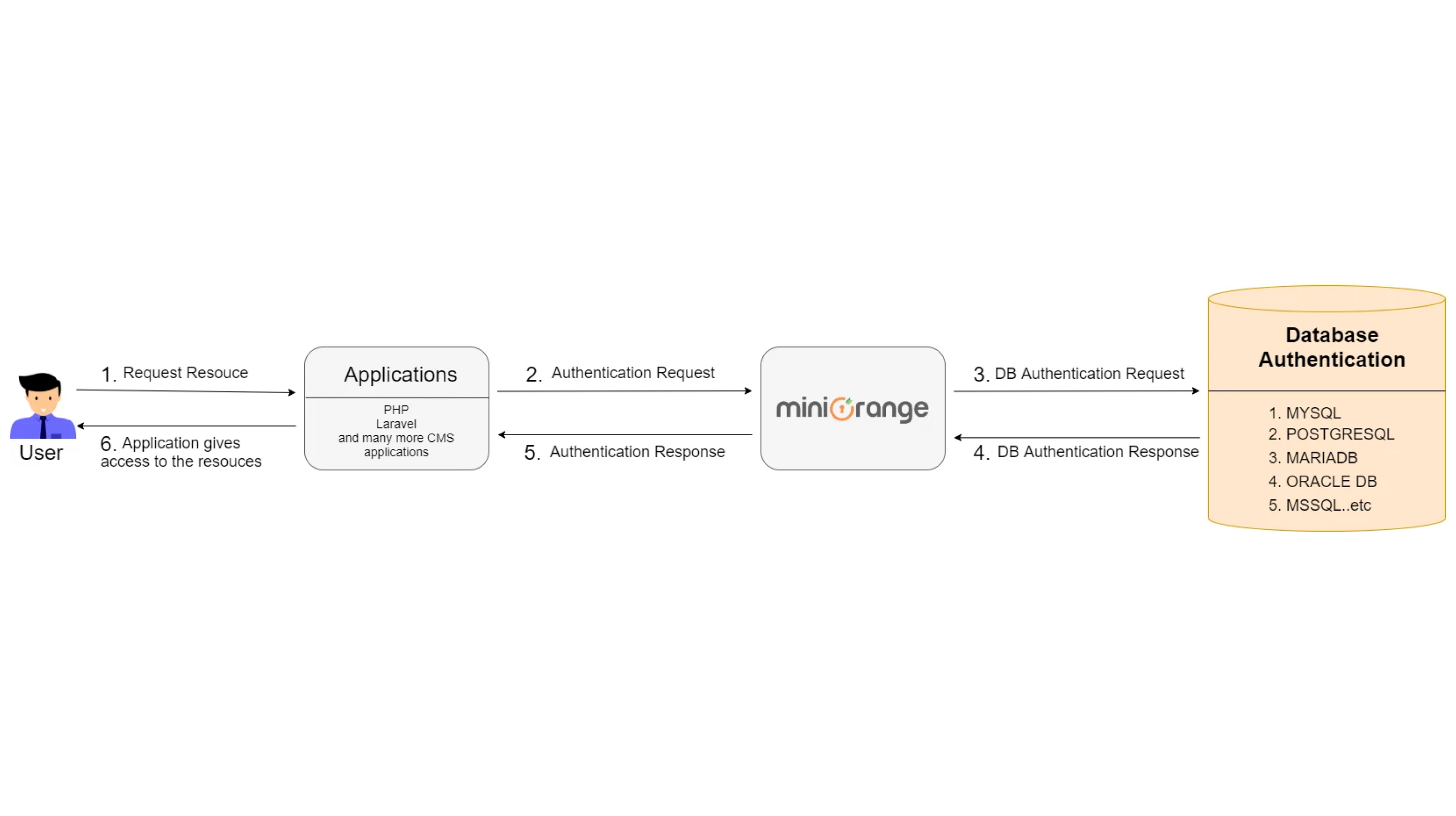
Custom Database connections act as a comprehensive login system so as to get user identity information from your own Database (legacy identity store) to authenticate users. It starts with a process of integrating a database with IDP which creates an interface between your IDP and Database. IDP, after connecting, lets the Database act as an Identity Source to authenticate users once a user logs in or SSO into an application or website. Despite acting as an Identity Source, the Identity platform authenticates the user using their email ID/Username and password stored during a custom database configured within the IDP. When a user tries to SSO/login into the service using their credentials, a scripted query is implemented by the configured IDP on the corresponding Database to see the entered login credentials. If a match of the login credentials is found within the database, the user is authenticated and a session is made within the IDP. Here on, users can Single Sign-On into any of the applications which are configured with their IDP.
Custom Databases are often any of your SQL Server, MySQL server on the other management system during a local environment. Similarly, in API as Authentication Source the users are authenticated using their email ID/Username and password stored during a custom database. The sole difference here is that rather than configuring the custom database within the IDP, API endpoints are configured within the IDP. This helps the user to authenticate the user without exposing the database to IDP.
miniOrange provides a special provision to authenticate your Users in two variant ways :
- Using your own organizational user store / Database
- Using miniOrange as user store / Database
Using your own user store
If you’ve got an existing user store or wish to store user credentials on your own server without moving user identities, miniOrange enables you to attach to a custom database or repository and use it as the identity provider. With this, your database remains private within the organization’s premises providing user authentication services. miniOrange uses the database just for authentication purposes, and any other crucial information stays within the database, maintaining the user’s privacy and avoids moving the user’s data to any third-party application.
If there’s a requirement to send another attribute during authentication of the user, data is directly picked from the database without getting saved in miniOrange and obtained to the respective application.
Essentially, you can connect to any kind of database or web service with miniOrange’s Custom Database Connection. miniOrange allows you to make Custom Database connections for many commonly-used databases, including:
- MongoDB
- MySQL
- Oracle DB
- Maria DB
- PostgreSQL
- SQL Server
- Windows Azure SQL Database
- Web services accessed via Basic Auth
Using miniOrange as user store (miniOrange as IDP)
In this use case, miniOrange provides a secure database infrastructure for organizations to store users’ data. Here on when an existing user tries to log in to a specific service, it coordinates with the database for authentication. But when a new user tries to access data the user profile is made in miniOrange which auto-syncs with the organizational premise database. Using miniOrange as IDP, organizations can easily authenticate their users since all data is stored in miniOrange.
Considering security, Passwords are never stored by miniOrange IDP. Alongside IDP services, varying levels of security requirements can also be enforced for User Authentication which includes: Multi-Factor Authentication, Strong Password, Adaptive Authentication, etc.
Pros and Cons of integrating Database as Identity Source
This is how you can easily setup a Custom Database Connection with miniOrange IDP to securely and efficiently handle your user identities.
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| Security – As user information is stored in organizational premises only, no data is shared with third-party applications. This minimizes the danger of security loopholes. | Dependency on Application security – As IDP handles the general process, reliability on IDP increases. |
| No migration needed – As authentication directly occurs through your database/user store itself, there’s no need to migrate your users into IDP for authentication. | |
| Easy On-boarding/Off-Boarding – As the user’s information is stored and interlinked with the user-store, you can add/remove users accordingly. | |
| Minimized disturbance or inconvenience – As users don’t have to create new accounts or find a replacement environment within the IDP for authentication, they will continue working with any disturbance. | |
| Privacy – miniOrange keeps no stone unturned to the very fact that your user confidential data remains private to your own database. |
Further Reading
Author




Leave a Comment