What is RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service)?
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) is a networking protocol used to manage Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) for remote users who access a network service. It provides a centralized means of managing network access control and can be used to authenticate users connecting to a network through a variety of devices, including routers, firewalls, and VPNs.
The RADIUS protocol uses a RADIUS Server and RADIUS Clients.
A RADIUS server is a central server that provides authentication and authorization services for remote users who access a network. It receives authentication requests from RADIUS clients, such as routers, firewalls, or VPNs, verifies the credentials of the user, and returns an authorization decision to the client.
A RADIUS client, on the other hand, is a device that sends authentication requests to the RADIUS server. The client acts as the intermediary between the remote user and the RADIUS server and is responsible for forwarding user credentials to the server for verification and receiving authorization decisions from the server.
In summary, a RADIUS server provides AAA services, while a RADIUS client acts as a requestor of these services for remote users.
How does RADIUS Server Authentication work?
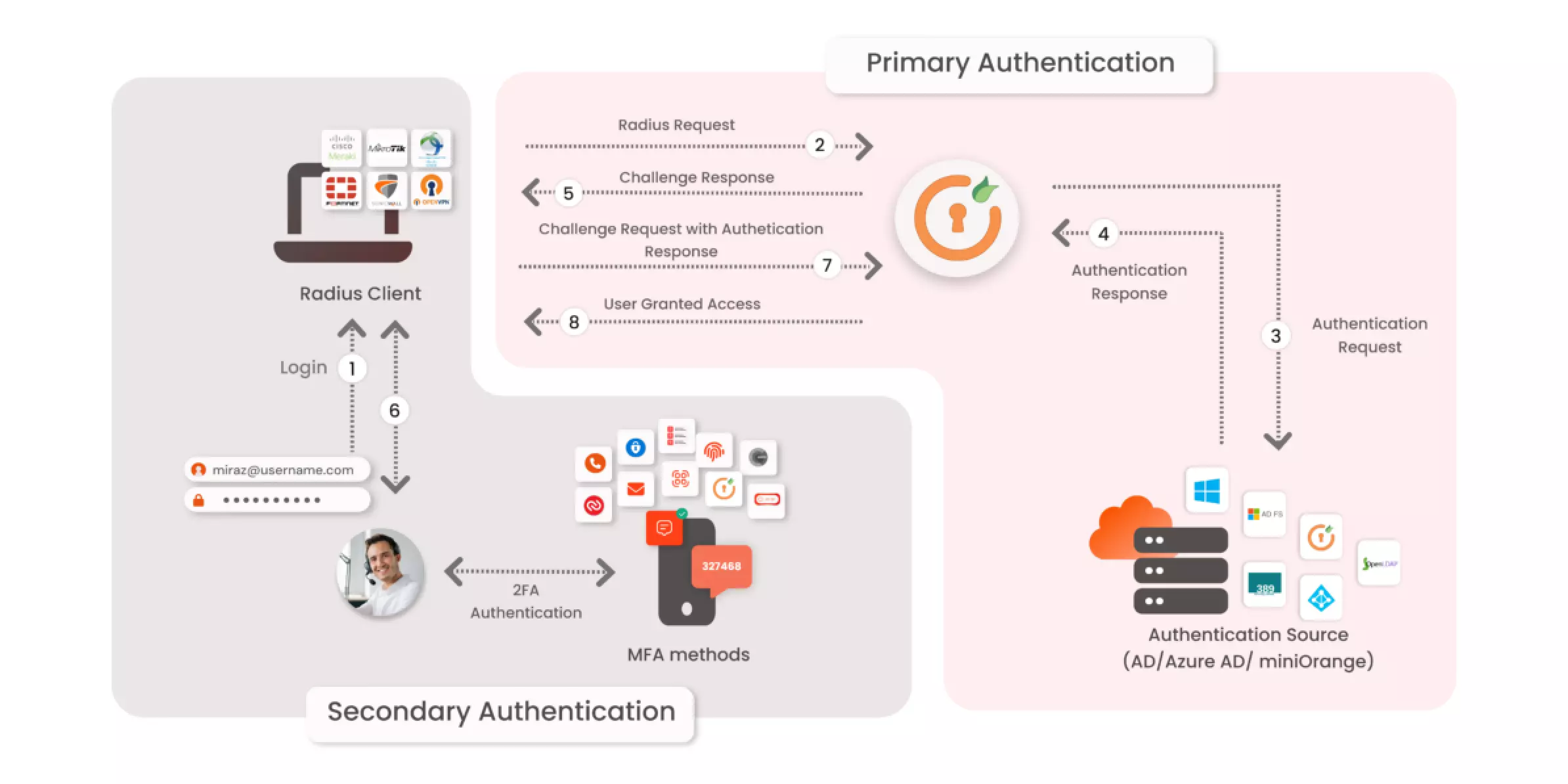
The RADIUS server authenticates a user by verifying their credentials against a database. The RADIUS client sends its credentials to the RADIUS server, which then authenticates them against an authentication database. If the credentials are valid, authorization information is returned to the client. This can include access control lists (ACLs), which specify which networks or resources each user has access to.
- In the first step, the RADIUS Client tries to authenticate itself using its user credentials.
- The Client then sends an Access-Request message to the RADIUS Server, which contains a username and password.
- The RADIUS Server uses the information contained in the request to authenticate users against an external database (such as Active Directory).
- If the RADIUS Server finds a match, it extracts additional details of that user from its database.
- The RADIUS server checks if there is an access policy or a profile that matches the user credentials. If one is found, MFA (if enabled) will be prompted and an Access-Challenge request sent.
- The response to the Access Challenge request will be provided by entering an OTP or accepting a push notification. The Radius server will validate that response.
- If the RADIUS Server can validate the response, it sends an Access-Accept message back to your device.
- If the response from the server does not match a policy or is invalid, then RADIUS returns an Access-Reject message and ends the transaction. The user will be denied access to the system.
- The Access-Accept message has a Filter ID attribute and a shared secret. If the RADIUS Client does not recognize the Shared Secret, it rejects the message.
- If the shared secret matches, the Client reads the value of the Filter ID attribute. The RADIUS Client then connects the user to a particular RADIUS Group using this Filter ID.
- The user is now able to connect to the network.
What is AAA?
AAA – Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
Authentication - This refers to the confirmation of the user which can be accomplished via presenting identity and credentials (for example: username and password or OTP or digital certificates.)
Authorization - This refers to the granting of specific types of services or resources based on the authentication process of the user. This helps in giving restricted permissions to the users. These restrictions may be based on the physical location, IP address, or time of access.
Accounting - This refers to the tracking of consumption of resources by the users. This feature can be used independently of RADIUS authentication or authorization. This may be used for management, planning, billing, etc.
RADIUS Server Authentication methods
The RADIUS server supports various methods to authenticate users. When it is provided with the username and original password given by the user, it can support PAP, CHAP, MS-CHAP, EAP, EAP_TLS, UNIX login, and other authentication mechanisms.
PAP – Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) authentication uses the PPP configuration files and PAP database for setting up authentication. The operation of PAP is similar to the UNIX login program, though PAP does not grant shell access to the user.
CHAP – Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) authentication uses to challenge and response, which means that the authenticator challenges the caller (authenticates) to prove its identity. The challenge includes the unique ID generated by the authenticator and a random number. The caller uses the ID, random number, and its CHAP security credentials to generate the response (handshake) to send to the peer.
MS-CHAP – is the Microsoft version of the Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP). It is used as an authentication option in Microsoft’s implementation of the PPTP protocol for VPNs.
EAP – Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is an authentication framework, used in wireless networks and point-to-point connections.
Conclusion
A RADIUS Server eliminates the possibility of leaks of your private information to snooping outsiders and enables you to easily control members’ access levels. It can be implemented with minimal impact on the rest of your system.
Further Reading
Author




Leave a Comment