Privileged Access Management (PAM) is a crucial cybersecurity strategy that helps organizations protect their privileged accounts from cyber threats. With cybercriminals increasingly targeting privileged accounts to access networks and carry out malicious activities, privileged access management has become a top priority for businesses worldwide. These privileged accounts are crucial for managing IT environments and carrying out administrative tasks, are found everywhere within an organization, including traditional systems and cloud infrastructure.
The importance of implementing PAM best practices cannot be overstated. Privileged accounts, such as domain administrators, service accounts, application accounts, and root accounts, can become main targets for attackers. If these credentials are compromised, cybercriminals can exploit critical systems, alter data, change configurations, and even bring operations to a standstill.
For two consecutive years, Gartner has recognized privileged access management as the top IT security priority. In 2022, it was highlighted as one of the Top 7 Trends in Cybersecurity, particularly under Identity System Defense. Despite this focus, many organizations still struggle to maintain even basic privileged account management best practices, leaving them vulnerable to potential attacks.
Implementing effective privileged user management best practices not only protects sensitive data but also ensures attackers cannot operate undetected within an organization's network. Let us have a look at Top 10 privileged account management best practices that can help businesses to secure their critical accounts, reduce security risks, and protect their operations from disruption.
First, have a look at the four key pillars of the PAM solution to gain a clear understanding of the essential elements that require focus.
The 4 Pillars of Privileged Access Management
To effectively implement privileged access management (PAM) best practices, organizations must focus on four key pillars: Discover, Secure, Audit, and Automate. Each pillar plays a crucial role in strengthening the security of privileged accounts and ensuring that only authorized users have access to sensitive resources. Here’s a breakdown of these pillars and how they contribute to a robust PAM framework.
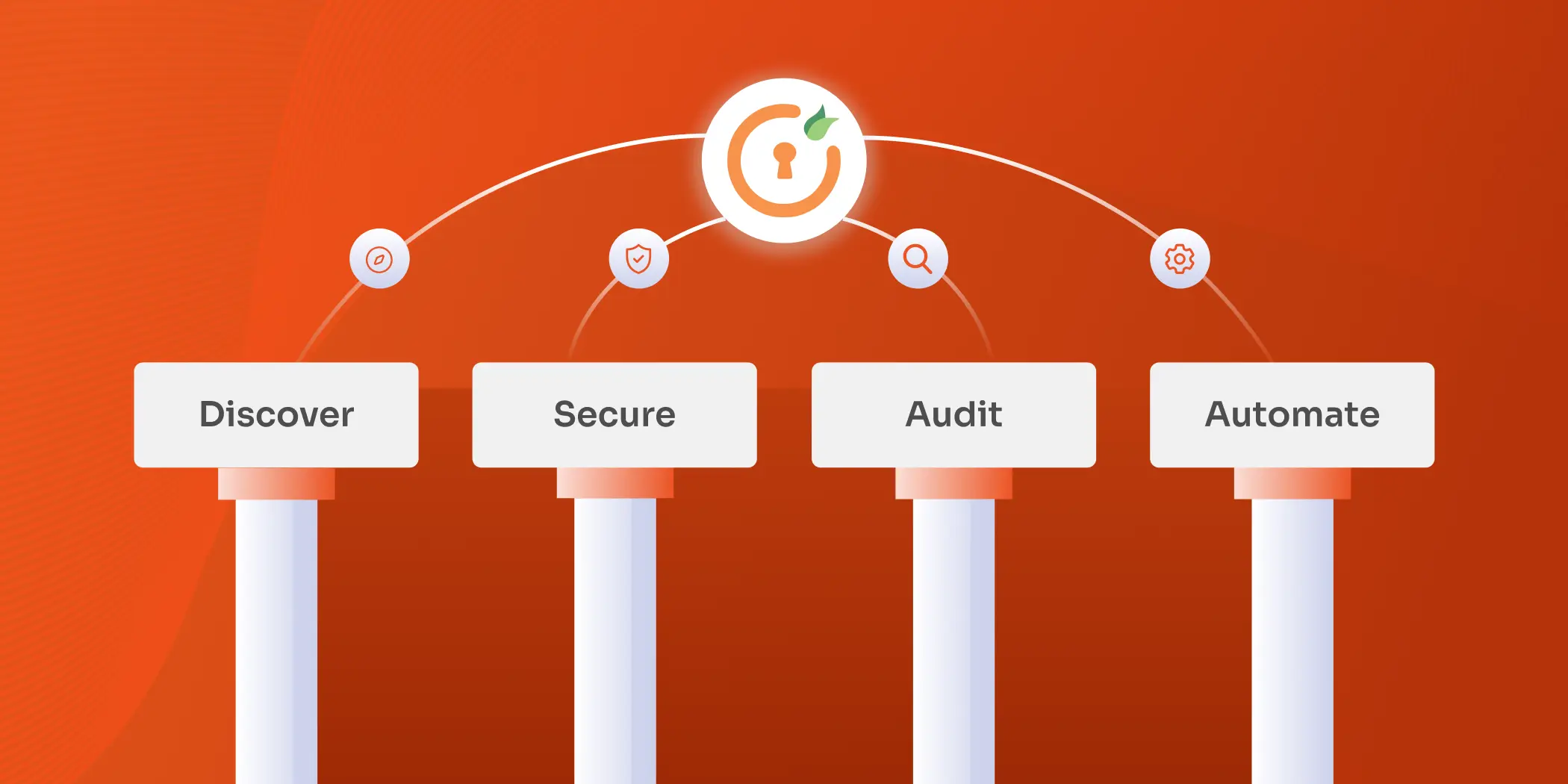
1. Discover
The first step in any privileged access management strategy is to identify all privileged accounts within the organization. This includes not just user accounts but also service accounts, application accounts, and shared accounts. Up-to-date information on all privileged accounts and their associated access rights is required. By identifying these accounts, organizations can gain visibility into who has access to what resources, allowing them to implement privileged access management best practices effectively. Discovering and cataloging these accounts is crucial for monitoring access and minimizing potential security gaps.
2. Secure
Once the privileged accounts are identified, the next step is to secure them with proper life cycle processes. This involves setting up strict access controls and continuously evaluating the access capabilities of each account based on its type. Effective privileged user management best practices include implementing strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), and securing passwords within an enterprise password vault to prevent unauthorized access. Regularly rotating and updating passwords, along with enforcing the least privilege principle, ensures that each account only has the permissions necessary to perform its tasks. Documenting these security measures creates a structured approach to privileged access, reducing the risk of exploitation.
3. Audit
Continuous auditing and monitoring are critical components of privileged account management best practices. Regularly reviewing privileged access helps detect any unauthorized activities or anomalies in user behavior. Utilizing session monitoring and logging tools provides detailed tracking of user activities, enabling organizations to identify suspicious behavior promptly. These logs not only serve as an early warning system for potential threats but also provide evidence during security incidents or audits. By integrating routine audits into the PAM Solution, organizations can maintain compliance, enforce security policies, and ensure that privileged access is managed effectively.
4. Automate
The final pillar of PAM best practices is to incorporate automation into the organization’s access management processes. Automation tools streamline and standardize access protocols, reducing the chances of human error and enhancing overall security. Implementing tools for just-in-time access allows organizations to grant temporary privileged access when needed, while identity governance and administration (IGA) tools help manage account life cycles efficiently. By automating key aspects of privileged access management, such as password rotation and access reviews, companies can enforce security policies consistently, respond to threats quickly, and maintain a high level of control over privileged accounts.
Top 10 best practices for Privileged Access Management (PAM)
1. Implement Zero Trust & Least Privilege Access
Zero Trust: This approach treats every user, device, and network as a potential threat, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the organization's network. Access is granted only after continuous verification of identity, device health, and other contextual factors. Zero Trust ensures that unauthorized users cannot move laterally within the network.
Least Privilege Access: This principle limits user permissions to the minimum necessary to complete their job functions. For example, if an employee only needs to access a specific database for their work, they should not have permission to modify system settings or view other databases. This reduces the attack surface and limits the potential damage in case of a breach. Implementing these policies together strengthens overall security and prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data.
2. Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Why MFA? Relying solely on passwords is risky, as they can be guessed, stolen, or compromised through phishing and social engineering attacks. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring additional verification, such as a one-time code sent to a mobile device or biometric authentication.
How to Implement: When users log in, they must provide at least two forms of verification (e.g., password and fingerprint). This ensures that even if an attacker acquires a user's password, they still cannot access the account without the secondary factor.
Employee Training: Beyond implementing MFA, organizations should train employees to recognize phishing attempts and social engineering tactics that can compromise login credentials. Proper training helps employees avoid falling victim to schemes designed to exploit MFA and strengthens the overall defense strategy.
3. Regularly Rotate and Expire Passwords
Frequent Changes: Regular password rotation (e.g., every 30-60-90 days) prevents long-term misuse of credentials. In case a password is compromised, frequent changes minimize the window of opportunity for attackers to exploit it.
Automatic Expiry: Configuring passwords to expire automatically enforces this practice and ensures that even dormant accounts do not pose a security risk. Passwords should not be reused, and each new password should be unique to reduce the risk of common passwords being cracked.
4. Monitor Privileged Activity
Why Monitor: Privileged accounts have the highest level of access, making them prime targets for attackers. Monitoring these accounts helps detect unusual activities, such as login attempts from unfamiliar locations or unauthorized access to critical systems.
How to Monitor: Use security information and event management (SIEM) tools to log and analyze privileged account activities. Setting up alerts for specific events, like failed login attempts or access to sensitive files, allows security teams to respond quickly to potential breaches.
5. Use Secure Password Storage
Encryption: Store passwords using strong encryption algorithms, such as AES-256. This ensures that even if the password storage is breached, the data is unreadable without the decryption key.
Password Management Tools: Utilize password vaults or managers specifically designed to store privileged credentials securely. These tools not only encrypt passwords but also allow for secure sharing and automated password rotation, reducing the risk of password exposure.
6. Conduct Regular Security Audits
Review Policies: Periodically review access controls, password policies, and security procedures to identify any weaknesses or non-compliance with the organization’s security standards.
Access Audit: Check who has access to what resources, especially privileged accounts, to ensure that only authorized personnel have the appropriate level of access. Audits can reveal unused accounts or excessive privileges, allowing you to take corrective actions, such as revoking unnecessary access.
Explore how miniOrange PAM Solution meets compliance regulations, click to learn more!
7. Limit Access to Sensitive Data
Access Controls: Implement access controls that limit exposure to sensitive information. Sensitive data, such as financial records or customer information, should only be accessible to users who need it for their specific roles.
Data Segmentation: Use data segmentation techniques, such as network segmentation or database partitioning, to isolate sensitive information. This containment strategy limits the potential damage of a breach by preventing attackers from easily accessing other parts of the system.
8. Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC Model: Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) allows access permissions to be assigned based on roles within the organization. For example, an employee in the finance department will have different access rights than someone in IT support. This helps maintain an organized access control system that is easy to manage and audit.
Granular Access Control in a PAM solution operates through an Access Control Policy, which allows restrictions at a highly detailed level. For example, a super admin can block users from running sensitive commands in PowerShell or Command Prompt (CMD), and also prevent users from running unauthorized applications on endpoints.
9. Use Privileged Session Management
Through Privileged Session Monitoring and Recording all privileged sessions to provide a detailed audit trail. This means capturing who accessed what resources, what actions were performed, and when. Such logs are invaluable for forensic analysis in the event of a security incident. Some tools offer real-time session monitoring and control features, allowing security administrators to terminate sessions if suspicious activity is detected. This proactive approach prevents unauthorized changes and ensures that privileged accounts are not misused.
10. Continuously Train and Educate Users
Security Awareness: Regularly conduct training sessions to keep employees informed about the latest security threats and best practices for managing privileged accounts. They should understand the importance of strong passwords, MFA, and be able to recognize phishing scams.
Ongoing Education: Since attack methods constantly evolve, education should be continuous. Training should also include handling sophisticated social engineering attacks and addressing MFA fatigue. Educating employees empowers them to act as a frontline defense against potential breaches.
NEXT STEP!
By adhering to these best practices, organizations can greatly enhance their security posture, effectively safeguarding privileged accounts and protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access and potential breaches. To ensure robust and up-to-date defenses, consider leveraging miniOrange's advanced Privileged Access Management solutions, tailored to meet your specific security needs in 2024 and beyond.
Author




Leave a Comment