Are you tired of constantly worrying about unauthorized access to your company’s sensitive data? You’re not alone. 74% of all data breaches involve access to a privileged account, highlighting a critical vulnerability in many organizations. Imagine the chaos and financial loss that can result from just one breach. This is where robust User Access Management (UAM) comes into play, offering a solution to safeguard your data and ensure only the right people have access to the right resources at the right time.
Regulatory requirements such as GDPR and HIPAA demand strict control over data access. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and legal consequences.
In this article, we will see how User Access Management (UAM) ensures authorized access to resources, reducing data breaches and unauthorized access. Effective UAM enhances security, compliance, and operational efficiency, protecting sensitive information and maintaining a strong security posture.
Understanding User Access Management
What is User Access Management at its Core?
User management is a critical component of Identity and Access Management (IAM) that focuses on controlling and managing user access to an organization’s resources, such as systems, data, and networks. At its core, UAM ensures that the right individuals have the appropriate access to the right resources at the right time, thereby safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining regulatory compliance.
Key Components of User Access Management
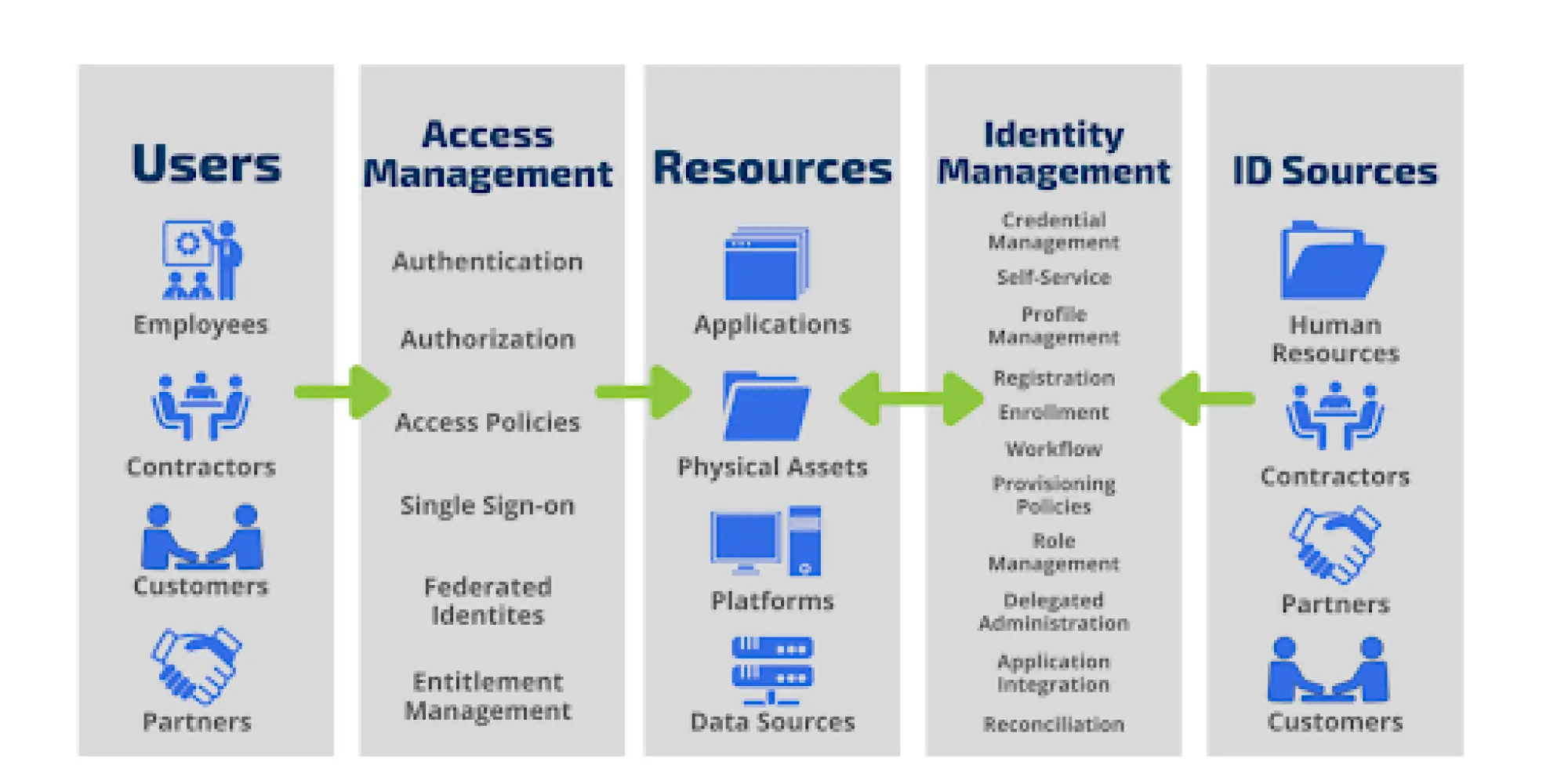
- Identity Verification: The process of confirming a user’s identity through authentication methods such as passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Access Provisioning: Granting access to resources based on predefined roles and permissions. This involves creating user accounts, assigning roles, and setting permissions.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): A method of restricting access based on the user’s role within the organization. Each role has specific permissions that define what resources the user can access and what actions they can perform.
- User Lifecycle Management: Managing user accounts throughout their lifecycle, from onboarding to offboarding. This includes creating, modifying, and deactivating user accounts as needed.
- Least Privilege Principle: Ensuring that users have the minimum level of access necessary to perform their job functions. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
- Access Reviews and Audits: Regularly reviewing and auditing user access to ensure that permissions are up-to-date and align with the user’s current role and responsibilities. This helps identify and mitigate any potential security risks.
The Relationship Between Identity Management and Access Management
Understanding the relationship between Identity Management and Access Management is crucial for building a secure and efficient IT environment. By effectively managing identities and controlling access, organizations can protect sensitive information, ensure compliance, and enhance overall security.
Identity Management (IdM) Identity Management is the process of identifying individuals within a system and managing their access to resources by associating user rights and restrictions with the established identity. It encompasses:
- Identity Creation: Establishing a digital identity for users, which includes attributes like username, password, and other personal information.
- Identity Maintenance: Updating and managing identity information throughout the user’s lifecycle.
- Identity Deletion: Removing identities when they are no longer needed.
Access Management (AM) Access Management focuses on controlling user access to resources based on their identity. It ensures that the right individuals access the right resources at the right times for the right reasons. Key components include:
- Authentication: Verifying the identity of a user (e.g., passwords, biometrics, multi-factor authentication).
- Authorization: Determining what resources an authenticated user can access and what actions they can perform.
- Access Control: Enforcing policies that govern access to resources.
Relationship Between IdM and AM
The relationship between Identity Management and Access Management is symbiotic and essential for robust security. Here’s how they interconnect:
- Foundation of Security: IdM provides the foundational identity data that AM relies on to make access decisions. Without accurate identity information, access control mechanisms cannot function effectively.
- Lifecycle Management: IdM manages the lifecycle of user identities, ensuring that access rights are updated as users join, move within, or leave an organization. AM uses this information to grant or revoke access in real-time.
- Policy Enforcement: IdM defines user roles and attributes, which AM uses to enforce access policies. For example, a user’s role in IdM might determine their access level in AM.
- Compliance and Auditing: Both IdM and AM play crucial roles in compliance with regulations and standards. IdM ensures that user identities are managed according to policies, while AM ensures that access to resources is compliant and auditable.
The Critical Role of User Access Management in Cybersecurity
Why Do Modern Organizations Need User Access Management?
User Access Management (UAM) is essential for modern organizations to enhance security, ensure compliance, improve efficiency, and drive growth.
- Enhanced Security
- Prevent Unauthorized Access: Reduces data breach risks.
- Minimize Insider Threats: Controls access to reduce insider threats.
- Compliance with Regulations
- Adherence to Standards: Ensures compliance with regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Audit Readiness: Provides logs and reports for easier audits.
- Operational Efficiency
- Streamlined Access: Automates access management to save time.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Simplifies user permissions management.
- Improved User Experience
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Access multiple applications with one set of credentials.
- Self-Service Portals: Users manage access requests and password resets.
- Scalability
- Adaptability: Scales with organizational growth.
- Cloud Integration: Integrates with cloud services for hybrid and remote work.
User Access Management Best Practices
Implementing the Principle of Least Privilege
- Grant Minimum Access: Users get only the access necessary for their job.
- Regular Reviews: Periodically audit permissions to ensure compliance.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions based on roles, not individuals.
- Just-In-Time Access: Provide temporary access for specific tasks.
- Segregation of Duties: Separate critical tasks to prevent fraud or error.
Regular Access Reviews and Audits
- Periodic Audits: Schedule regular reviews of user access rights.
- Automated Tools: Use IAM tools to streamline and automate audits.
- Compliance Checks: Ensure adherence to policies and regulations.
- Anomaly Detection: Identify and address unusual access patterns.
- Documentation: Maintain records of reviews and actions taken.
miniOrange User Access Management Solution
miniOrange offers a comprehensive User Access Management solution that includes:
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Seamless access to multiple applications with one set of credentials.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enhanced security through additional verification steps.
- User Provisioning: Automated user account creation, updates, and deactivation.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assigns permissions based on user roles.
- Audit and Compliance: Tracks and reports user activities for compliance purposes.
The Future of User Access Management
The future of user access management will be shaped by AI integration, biometric authentication, and decentralized identity management. These trends will enhance security, streamline processes, and provide user-centric solutions.
miniOrange offers a comprehensive user access management solution that includes Single Sign-On (SSO), Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and User Provisioning. These features help businesses secure their workforce, customers, and partners, ensuring seamless and secure access to resources.
Take control of your organization’s security today with miniOrange’s cutting-edge solutions. Request a demo now and experience the future of user access management!
Author


Leave a Comment