Cyberattacks and data breaches have been making headlines more frequently lately. Here are a few notable examples:
- The Real Estate Wealth Network, a New York-based online real estate education platform, inadvertently exposed over 1.5 billion records from their database. The unprotected database, containing approximately 1.16 TB of data, was left vulnerable due to non-password-protected folders and system access.
- In April 2022, a former employee of Cash App managed to download information from over 8 million users through the Cash App Investing feature. This breach occurred because the company failed to properly control access properly, even though the individual was no longer employed there.
Both incidents highlight a critical vulnerability: inadequate access control. Monitoring and controlling who has access to critical data has never been more crucial. One of the most effective ways to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive information is through a robust access control system.
But what exactly is an access control system, and how can it safeguard your organization's sensitive data? Let’s explore the fundamentals of access control in cybersecurity and understand why every organization should prioritize it.
What is an Access Control in Cybersecurity?
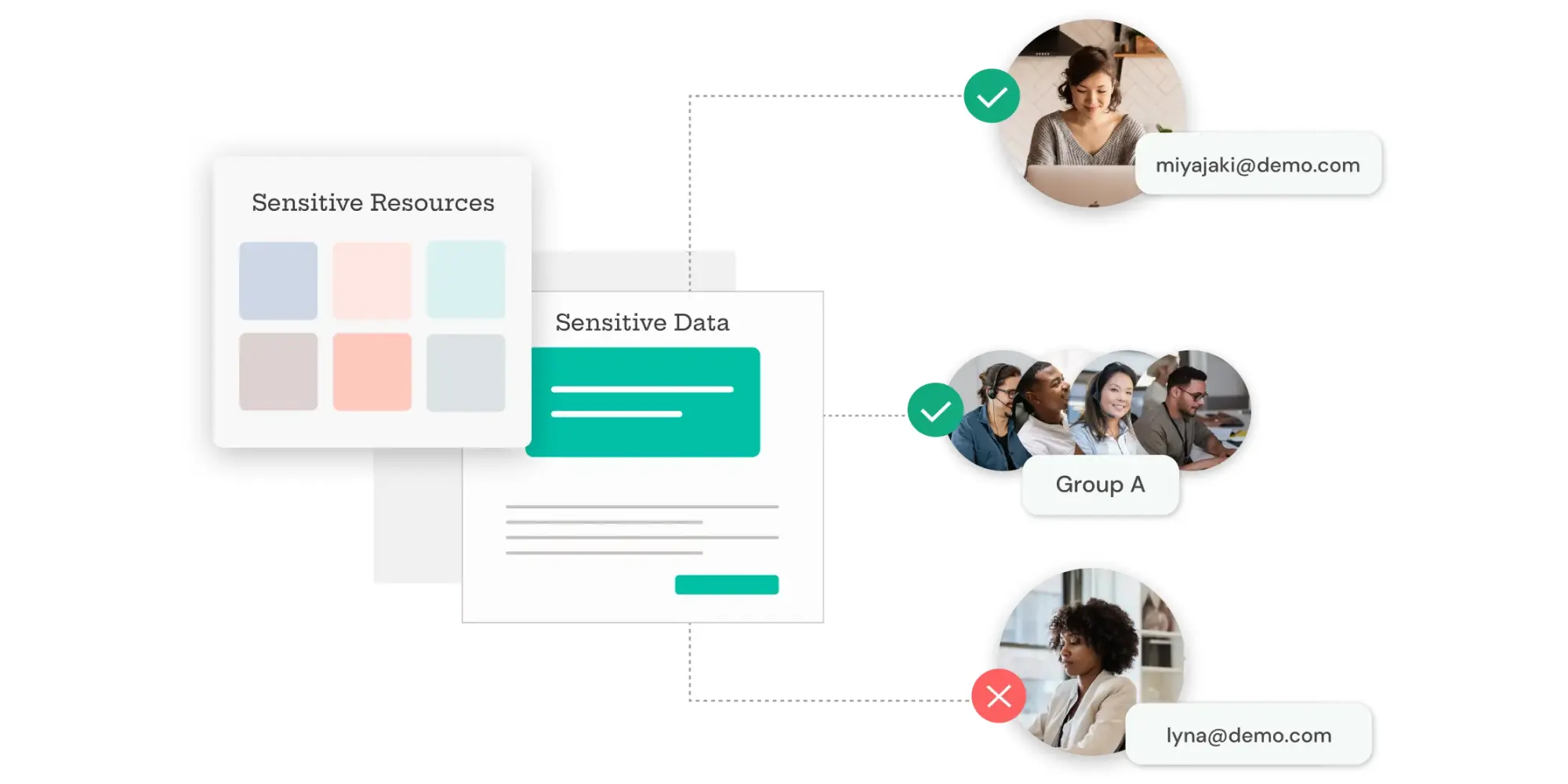
An access control system is a fundamental component of cybersecurity that ensures only authorized individuals can access specific areas or data within a system. It verifies users’ identities and grants access based on their credentials, such as passwords, biometric data, or multi-factor authentication (MFA).
In the context of cybersecurity, access control refers to the methods and technologies used to regulate who can view or interact with resources in a digital environment. This process is crucial for preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information and systems, thereby safeguarding an organization’s data.
Access control typically involves three key steps: identifying users, authenticating their credentials, and authorizing them to access specific resources. By enforcing these measures, organizations can ensure that users only have access to the data or systems they are permitted to use, reducing the risk of data breaches or other security incidents.
But how does an access control system help safeguard data? To get an answer to this question, we need to understand the workings of access control software.
How Does Access Control Solution Work?
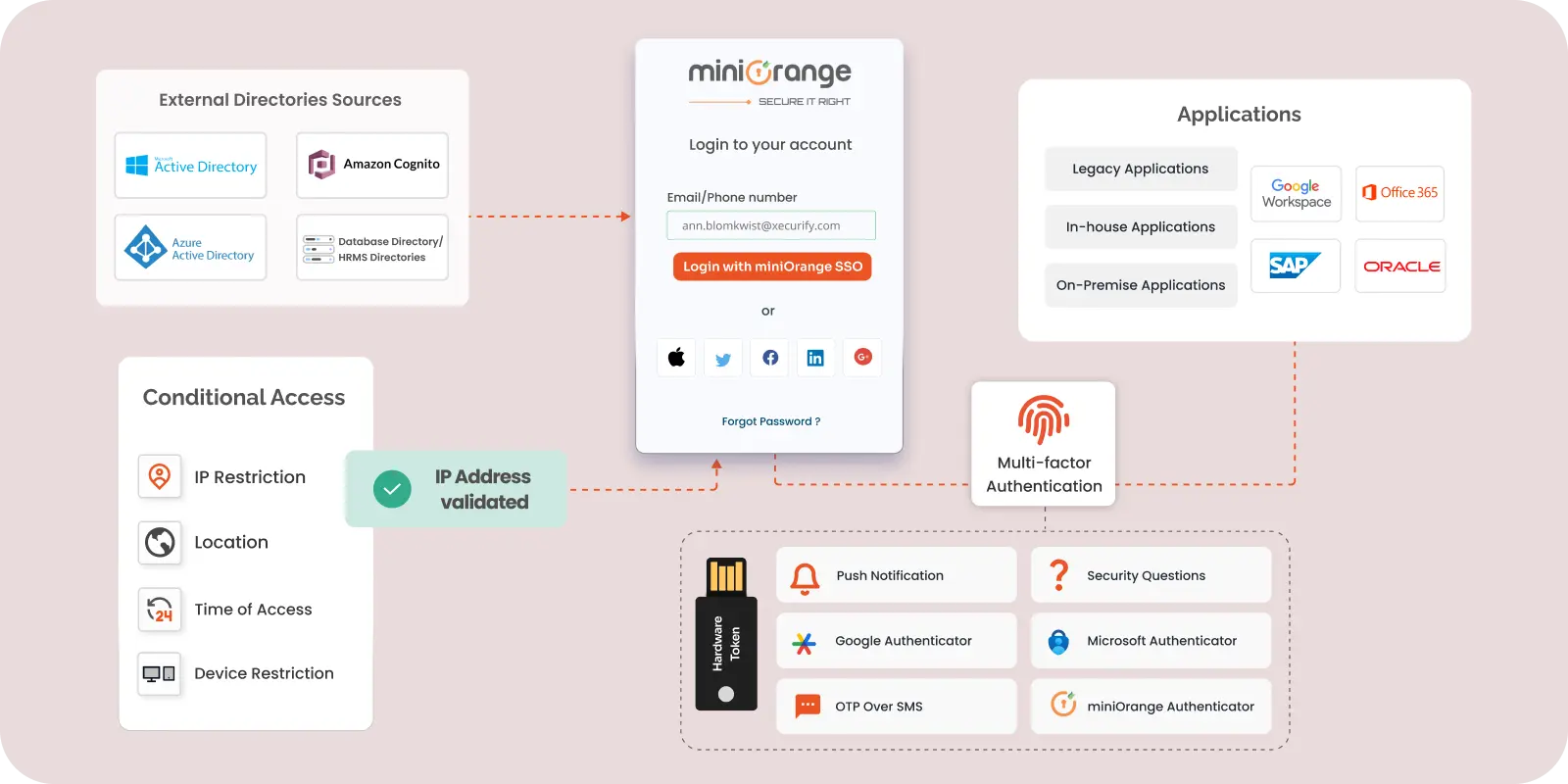
Access controls verify an individual or entity’s identity and determine their access level and actions based on their username or IP address. Directory services and protocols like LDAP and SAML help manage authentication and authorization, allowing secure access to resources such as applications and web servers.
Let’s go through the step-by-step workflow of the access control system:
Authentication: Verifies the user's identity through methods like passwords, biometrics, or security tokens.
Permission Checking: Compares the user's credentials against predefined access rules or roles.
Access Decision: Grants or denies access based on the user's permissions and the resource's access rules.
Resource Protection: Ensures only authorized users can interact with sensitive data, systems, or physical spaces.
Security Maintenance: Helps protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats, preserving the organization’s security integrity.
This is the basic mechanism of working of an access control system. But did you know that different types of solutions can cater to different requirements? Well, when it comes to security, we cannot follow the one-size-fits-all approach. Let’s take a walk through different types of access control solutions,
Types of Access Control in Cybersecurity
Access control software comes in various types and is often integrated into a broader identity and access management strategy. These tools can be deployed on-premises, in the cloud, or both, and can manage internal access or customer access. Types of access control solutions include:
Discretionary Access Control (DAC): In this model, the owner of the resource decides who can access it. Users are given the flexibility to control access to their own data or resources.
Mandatory Access Control (MAC): Here, access rights are regulated by a central authority based on the classification of information and the clearance of the user. It is commonly used in environments requiring high security, such as government agencies.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Access rights are assigned based on the user’s role within the organization. This is one of the most commonly used models in enterprises because it simplifies user permissions management.
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC): This model uses attributes (such as user characteristics, resource types, and environmental factors) to determine access. ABAC offers more granular control compared to RBAC.
Is access control only limited to controlling access to solutions? What is the broader importance of access control solutions? Let me break this news to you - Access control plays a crucial role in regulatory compliance too.
Importance of Access Control in Regulatory Compliance
Effective access control is crucial for regulatory compliance, ensuring that sensitive data is protected according to industry standards. Compliance with regulations like PCI DSS, HIPAA, SOC2, and ISO 27001 is vital for safeguarding information and avoiding penalties.
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): Access control is crucial in PCI DSS for protecting cardholder data by limiting access to authorized personnel only, ensuring secure transactions, and maintaining compliance with stringent data security requirements.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): In HIPAA, access control safeguards patient information by restricting access to authorized users, ensuring that healthcare providers comply with privacy and security standards, and protecting sensitive health data from unauthorized access.
SOC 2 (System and Organization Controls 2): Access control in SOC 2 ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data, maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of information systems, and demonstrating adherence to strict data protection and privacy practices.
ISO 27001 (International Organization for Standardization 27001): Access control in ISO 27001 is vital for protecting information assets by implementing stringent access policies, ensuring authorized access only, and aligning with global standards for information security management.
Challenges of Access Control
Access control systems play a crucial role in cybersecurity, but they face significant challenges. Effective management of these systems requires addressing various complexities to ensure robust protection and compliance. Key challenges include:
Complex Permission Management: Handling intricate permission structures and frequent updates can be challenging, particularly in large organizations.
System Integration Issues: Integrating access control with legacy systems complicates the implementation of consistent security policies.
Scalability Concerns: Adjusting access levels and roles as organizations grow can strain existing systems.
User Convenience vs. Security: Ensuring access control measures don’t impede productivity while maintaining robust security is difficult.
Adaptation to Evolving Threats: Constantly updating access controls to address new and emerging threats is essential but challenging.
Regulatory Compliance: Maintaining adherence to changing regulatory standards requires ongoing vigilance and adjustments.
Access Control Software Components
While access control software secures sensitive resources by managing who can access the data, its key components ensure comprehensive protection and streamlined user experiences.
Authentication: Authentication, as mentioned above, verifies user identities through credentials like passwords, biometrics, or multi-factor authentication, ensuring that only legitimate users gain entry to the system.
Authorization: While authentication and authorization may sound similar, the latter determines what authenticated users can access, granting permissions based on roles or policies to control access to resources and maintain security.
Access: Access ensures that users can efficiently reach the resources they are authorized to use, enabling seamless operations while keeping unauthorized entities out.
User Management: User management handles the creation, maintenance, and deactivation of user accounts, ensuring that access is consistently aligned with organizational roles and responsibilities.
Audit: Auditing, tracking, and logging user activities within the system is crucial. This provides essential data for security reviews, compliance, and the identification of suspicious or unauthorized actions.
What Should You Expect from Access Control Solutions?
Now that you know what an access control solution is and how it works, let’s go through a few tools and features that make a robust access control software that can secure, streamline, and simplify user access to organizational resources.
Single Sign-On (SSO): Allowing users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials reduces the need to remember multiple passwords, enhances user experience, and strengthens security by centralizing authentication.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): An extra layer of security cannot harm! MFA requires users to provide multiple verification forms—such as a password, token, and biometrics before gaining access.
User Lifecycle Management : Automating the entire user journey from onboarding to offboarding ensures that user access rights are aligned with their role and updated as they change positions or leave the organization, reducing security risks and saving time.
Password Management: Password management simplifies the creation, storage, and reset of passwords, ensuring that users adhere to strong password policies. It reduces the risk of password-related breaches by promoting secure password practices across the organization.
User Provisioning/Deprovisioning: Automating the process of granting and revoking user access to systems and applications allows the users to have appropriate access from the start and that access is promptly removed when no longer needed, minimizing the potential for unauthorized access.
Reporting and Monitoring: Comprehensive reporting and monitoring tools track user activities, access patterns, and potential security incidents. These features provide valuable insights for compliance audits, security reviews, and identifying any unusual behavior that could indicate a threat.
Unlock the Full Potential of Your Security with miniOrange Access Control Solutions
In today’s complex IT environments, ensuring robust access control is essential for maintaining security and regulatory compliance. miniOrange offers comprehensive solutions to address every component of access control, making your organization safer and more efficient.
We specialize in providing comprehensive identity and access solutions designed to safeguard your most valuable assets. Prioritizing access control is not just a best practice; it’s a vital component of your cybersecurity strategy. Investing in a comprehensive access control system today with miniOrange’s expert solutions can save your organization from the costly and damaging consequences of unauthorized access tomorrow.
Conclusion
In a world where cyber threats and data breaches are increasingly common, implementing a robust access control system is more critical than ever. By carefully managing who can access your sensitive information and systems, you not only protect your organization from potential security threats but also enhance overall data integrity and privacy.
Author



Leave a Comment