What is ADFS?
Active Directory Federation Service (ADFS) is a software component developed by Microsoft to provide Single Sign-On (SSO) authorization service to users on Windows Server Operating Systems. ADFS allows users across organizational boundaries to access applications on Windows Server Operating Systems using a single set of login credentials.
ADFS makes use of the claims-based Access Control Authorization model to ensure security across applications using the federated identity. Claims-based authentication is a process in which a user is identified by a set of claims related to their identity. The claims are packaged into a secure token by the identity provider.
How does ADFS work?
The authentication process using the Active Directory Federation Service (ADFS), takes place in the following steps:
- The user navigates to a service, for example, a partner-company website (http://example.com) to obtain pricing or product details.
- The website requests an authentication token.
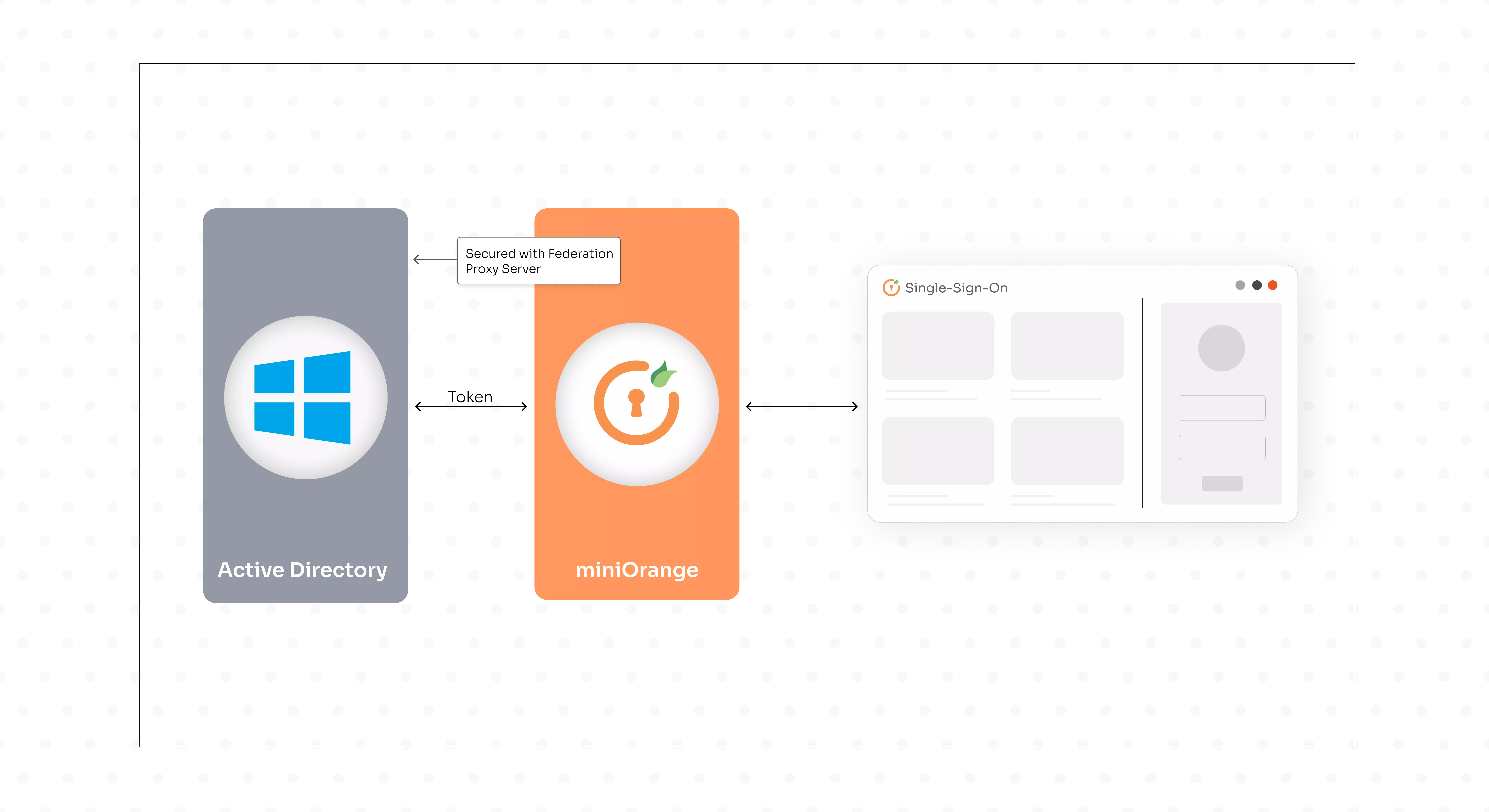
- User requests token from the ADFS server.
- ADFS server issues token containing user’s set of claims.
- User forwards token to the partner-company website.
- The website grants authorization access to the user.
What are the components of ADFS?
- Active Directory: The Identity Information which is to be used by ADFS is stored on the Active Directory.
- Federation Server: It contains the tools needed to manage federated trusts between business partners. It processes authentication requests coming in from external users and hosts a security token service that issues tokens for claims based on verification of credentials from AD.
- Federation Server Proxy: The Proxy is deployed on the extranet of the organization, to which external clients connect when requesting a security token. It forwards these requests to the Federation Server. The Federation server is not exposed directly to the internet to prevent security risks.
- ADFS Web Server: It hosts the ADFS Web Agent which manages the security tokens and authentication cookies sent to it for authentication purposes.
Why ADFS is used by organizations?
Using Active Directory (AD) in the connected online world creates authentication challenges. AD cannot authenticate users who try to access integrated applications externally. In the modern workplace, users often need to access applications that are not owned or managed by their organization’s AD. ADFS is able to resolve and simplify these third-party authentication challenges.
ADFS allows users from one organization to access applications of partner organizations using the standard credentials of their organization’s Active Directory (AD). ADFS also lets users access AD-integrated applications while working remotely using their standard organizational AD credentials via a web interface. When establishing a partnership to use another organization’s web applications, ADFS provides a central place to manage and audit the employee identity information that is shared with their organization’s partners.
Over 90% of organizations use Active Directory, which means many use ADFS as well.
ADFS can be used in the below scenarios
- Single Sign-On (SSO): ADFS can be used to provide Single Sign-On (SSO) authorization to users who want to access applications located in different networks or organizations. It provides seamless Single Sign-On (SSO) access to Internet-facing applications or services.
- Identity Federation (Identity Management): Federated Identity is a concept where a user’s identity is centralized. This makes Identity Management easier. Identity Management is done to maintain security while keeping the costs associated with managing user identities, low.
ADFS Office 365 example
- Office 365 uses an Active Directory environment wherein a dedicated domain is created on the cloud for each user’s Office 365 subscription.
- ADFS is used here by setting up directory synchronization (DirSyc tool) that creates accounts in Microsoft’s domain matching the accounts within the user’s domain.
- A user can select accounts that should be synchronized in the AD.
What are the limitations of ADFS?
- Maintenance Costs: ADFS generates a high cost of maintenance which consists of infrastructure maintenance, management of multiple federations, SSL certificate costs.
- ADFS Complexity: Adding an application or system to an ADFS service is complex and time-consuming. It doesn’t have a user-friendly management dashboard for managing users, groups, and authentication policies.
- ADFS Security issue: ADFS runs on Windows Server, that have more security issues like vulnerability to malware and other security related errors.
- ADFS does not allow file-sharing or printing using print servers.
- ADFS cannot access Active Directory resources.
- ADFS does not support Remote Desktop connections.
ADFS Vs miniOrange IDP
| Features | ADFS | miniOrange IDP |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-Protocol support | Supports limited protocol (SAML 2.0, WS-Federation & OAuth 2.0) | Fully Supports all protocols for Authentication |
| MFA (Multi-factor Authentication) | It supports limited MFA methods | It supports 15+ MFA methods |
| Single Sign-On into Mobile Apps | Doesn’t support | It supports SSO into Mobile Apps |
| Adaptive Authentication | Doesn’t support | It supports |
| JWT | Doesn’t support | It supports |
Related Articles of ADFS Integration
Author




Leave a Comment