What is Kerberos ?
Users traditionally submit a password to get access to computer systems. The problem with this authentication mechanism is that if hackers get a hold of the password, they can assume the user’s identity and access a network within an enterprise. There must be a better approach for businesses to safeguard their users and systems. Herein lies the role of the Kerberos authentication protocol.
A Kerberos authentication system acts as a gateway for users to access the internet. As a result, it aids in preventing online intruders from accessing a private network. Cybercriminals will find it considerably harder to access your network thanks to the robust cryptography and third-party ticket authorization.
Microsoft Windows presently uses Kerberos authentication as its standard authorization method. Kerberos is also supported by Apple OS, FreeBSD, UNIX, and Linux. Kerberos has drastically increased the security of the internet and its users while allowing users to perform more tasks online and in the office without risking their safety.
What makes the Kerberos authentication protocol different from others is a couple of strong security-based features.
- Passwords are never sent across the network.
- Encryption keys are never directly exchanged.
- The application can mutually authenticate each other.
- Many organizations use it as the basis for Active Directory SSO.
Kerberos terms :
- Kerberos Realm : Group of systems over which Kerberos has authority to authenticate the user to a service.
- Principal : Unique identity(user/service/application).
- Clients/Users : a process that accesses a service on the behalf of a user. Can have multiple clients or users within a realm.
- Service : Something the user wants to gain access to.
- KDC (Kerberos Key Description Center) : Supplies tickets and generates temporary session keys that allow a user to securely authenticate to a service. The KDC stores all the secret symmetric keys for users and services.
How does Kerberos work ?
Users, workstations, and services that use Kerberos rely solely on the KDC, which runs as a single process and handles both tickets granting and authentication. All parties can authenticate themselves using KDC “tickets” which enables nodes to do so safely. In order to protect the messages, the Kerberos authentication procedure uses a traditional shared secret cryptography. This prevents packets moving across the network from being read or altered.
What are the Kerberos Authentication steps ?
There are 2 servers that enable Kerberos to work. An authentication server, and a ticket-granting server.
- Authentication Server : Confirms that a known user is making an access request and gives a ticket-granting ticket.
- Ticket granting Server : Confirms that a user is making an access request to a known service and gives service tickets.
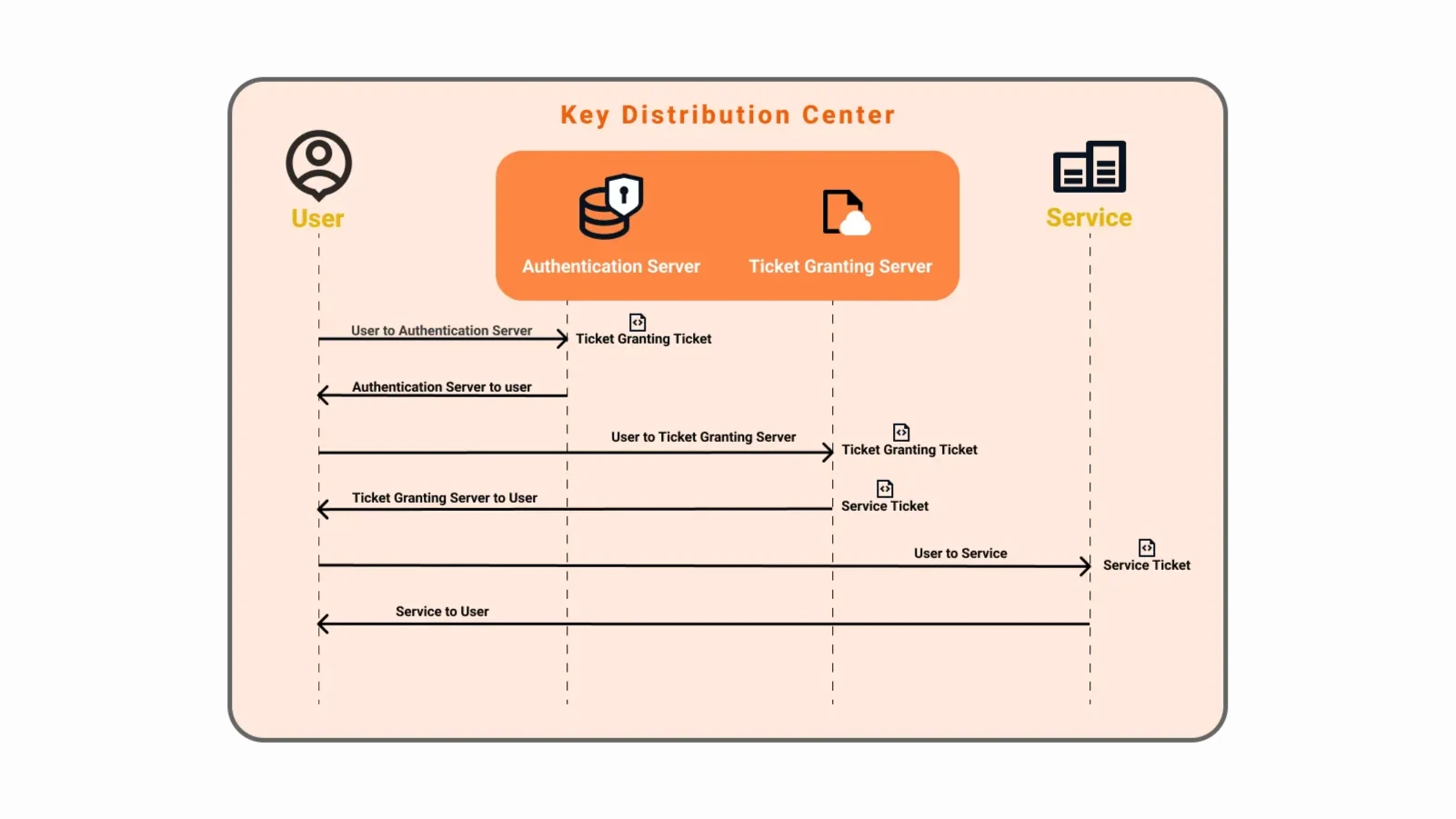
Step 1 : User sends a request to the authentication server mentioning they want to access a service. The Authentication service is validated if the service is coming from a known and grants a TGT: ticket-granting ticket.
Step 2 : The authentication server sends the TGT back to the user along with another message encrypted with the user’s secret key.
Step 3 : The user decrypts the message with their secret key and sends the TGT with some additional information to the Ticket Granting Server.
Step 4 : The ticket-granting server decrypts the TGT, performs some validations, and creates a service ticket (ST). This service ticket with some additional information is sent back to the User.
Step 5 : The user decrypts the message, creates some authenticator message, and sends the user authenticator and the service ticket to the service.
Step 6 : The service does its decryption, and validation and creates its own final authenticator message. This is sent back to the user. These messages allow the user and the server to mutually authenticate each other and securely distribute a symmetric service session key. This allows both the user and service to communicate, authentication information securely.
Benefits of Authenticating using Kerberos
- Passwords will never be sent across the network due to its extreme security. Only keys are permitted.
- Mutual authentication always takes place in order for the client and server to connect simultaneously and converse with the appropriate counterpart.
- The authentication is always valid and never expires.
- The internet standard is the only factor that matters.
- A large portion of the industry has embraced Kerberos since it offers security, and they are glad to employ its security protocol.
Author


Leave a Comment