What is SAML?
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is an open standard that enables Identity Providers (IdPs) to send authorization credentials to service providers (SP).
For standardized interactions between the identity provider and service providers, transactions through this protocol use Extensible Markup Language (XML). It is the link between a user’s identity authentication and their authorization to use a service.
SAML permits Single Sign-On (SSO). You may enable seamless access to resources and minimize unsafe password proliferation by making a variety of sites available with only one set of login credentials.
SAML 2.0 was adopted by the OASIS Consortium in 2005. The standard has evolved dramatically since 1.1, to the point that the versions are incompatible. Adoption of this protocol helps IT businesses to deploy SaaS solutions while still maintaining a secure federated identity management system.
How does SAML work?
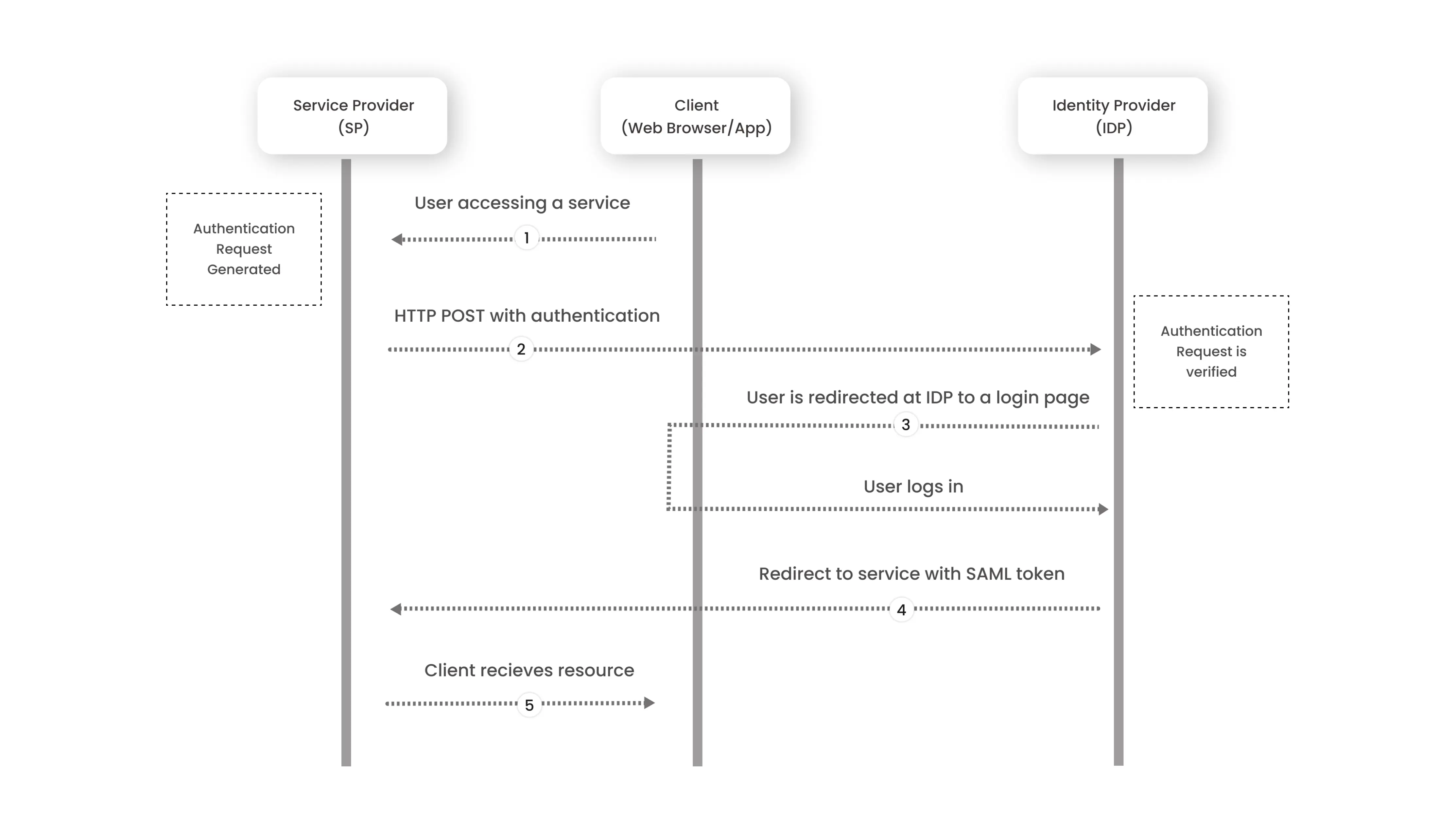
The identity provider and service providers exchange information about users, logins, and characteristics via SAML. When a user seeks to access services using Single Sign-On, the identity provider can provide SAML characteristics to the service provider. The service provider asks the identity provider for authorization and authentication. The user just has to log in once because both systems use the same language, SAML.
Each identity provider and service provider need to agree upon the configuration for SAML. Both IdP and SP need to have the exact configuration for a successful authentication flow.
What is OAuth?
OAuth which stands for “Open Authorization” is a technological standard for granting user permissions. It’s a method of transmitting authorization from one service to another without revealing the user’s actual credentials, such as username and password. A user can sign in on one platform and then be granted permission to execute activities and see data on another using OAuth. For authentication tokens, it utilizes its own XML documentation, although it can alternatively use JavaScript Object Notation (JSON).
It is a popular mechanism for passing authorization from a single sign-on (SSO) provider to another cloud application, although it may be used between any two apps. Even if this is one of the most actively used protocols, other protocols can also accomplish this purpose.
OAuth 2.0 is a significantly redesigned version of OAuth 1.0, using a different methodology. In the newer version, the consumer, service provider, and user roles of the older version are replaced by a client, authorization server, resource server, and resource owner roles.
How does OAuth work?
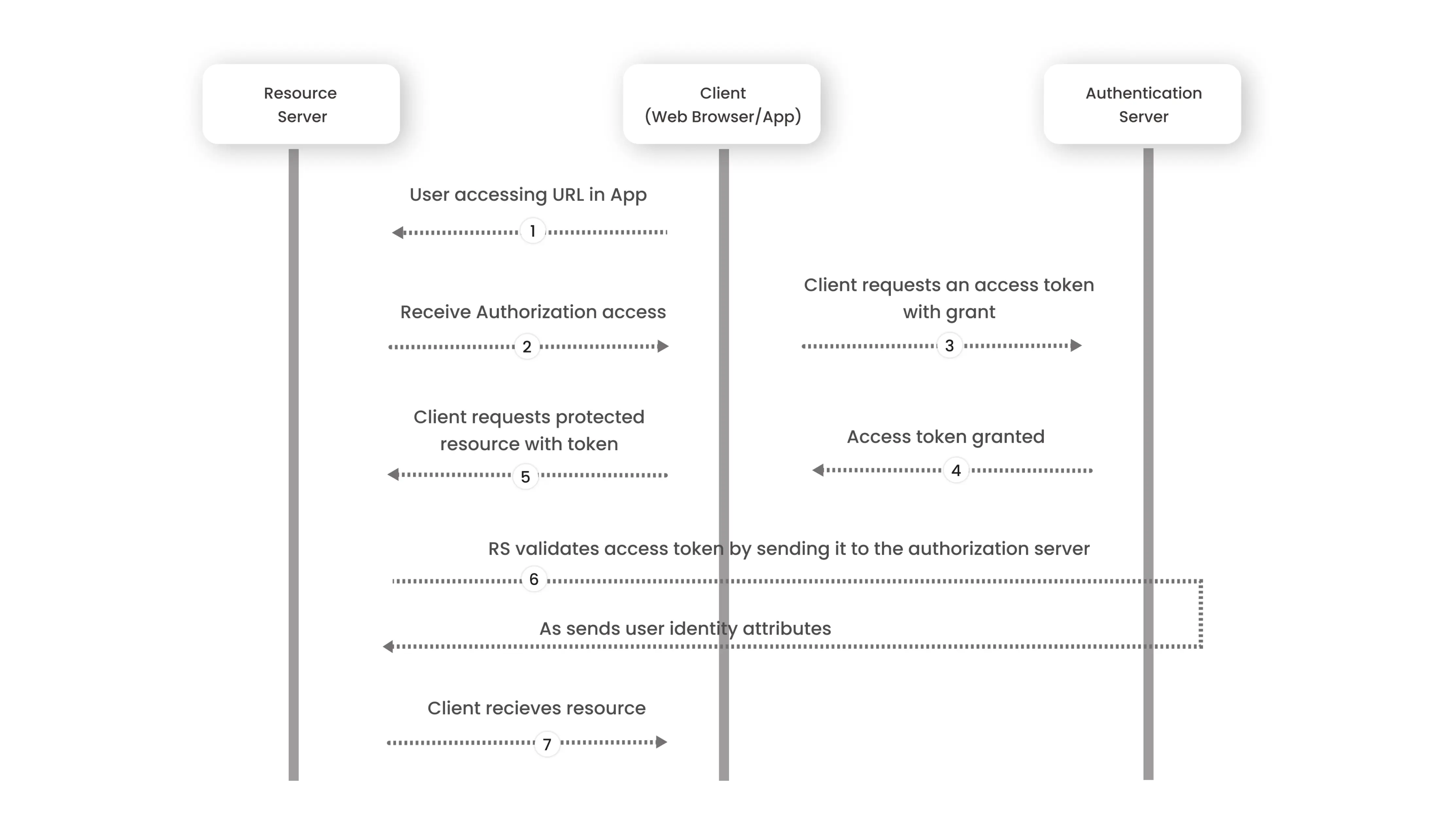
An OAuth Access Token transaction requires three players: the end-user, the application (API), and the resource (service provider that has your login credentials). The transaction starts when the user specifies that he or she wants to utilize the API.
Application asks permission: By submitting the user’s confirmed identity as proof, the application or API (application program interface) requests authorization from the resource.
Application requests Access Token: Without having to provide usernames or passwords, the resource grants an Access Token to the API when the authorization has been validated.
Application accesses resource: Tokens come with API access permissions. Permissions are called scopes, and each token has an approved scope for each API. The application can only access the resource to the degree that the scope permits.
SAML vs OAuth
Similarities:
Both of these authentication approaches allow SSO to eliminate unwanted usernames and passwords and also are based on open standards for verifying identities and granting access to protected resources via centralized administration. Easy enrollment and delegated user management help IT admins. The standards may even be mutually beneficial and promote interoperability. Authentication servers, for example, can acquire authorization grants from SAML-trusted IdPs via the OAuth assertion flow.
Differences:
While considering SAML vs OAuth, following two tools are used for distinct tasks:
- Authentication: The identity of the user is involved in this procedure. SAML works similarly to a home key. It allows you to use the facility.
- Authorization: The privileges of a user are involved in this procedure. OAuth is similar to the home rules that govern what a person can and cannot do while they are inside.
SAML Use Case:
SAML is commonly used for Single Sign-On in government and corporate applications (identity management), in which XML processing is widespread. Many government citizen ID programs use SAML (for example, UK Verify).
This protocol is used to manage users from a central location. You use this when you connect to your office computer and network. To get access to the network, users only need to input their credentials once.
OAuth Use Case:
Both in authorization and authentication roles, OAuth 2.0 is extensively utilized in user and corporate applications. It’s most commonly used to authorize access to RESTful APIs, where the usage of access tokens makes it simple and easy.
This protocol is also used to allow you to access one service from another without having to re-enter your login credentials. It is done by allowing you to use your credentials from one service to another.
The most prevalent use case for OAuth in the corporate world is in combination with Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions. It may be used to authorize users to use an application.
When we compare SAML vs OAuth, both are mutually beneficial. By using SAML to offer access to an application while utilizing OAuth to grant access to a protected resource, you may utilize both protocols at the same time. With either protocol or a mix of the two, you may use an identity provider or single sign-on (SSO) service accordingly.
FAQ
Is SAML based on OAuth?
In contrast to JWT, SAML is not dependent on OAuth and instead relies on an exchange of messages to validate in XML format. It’s more typically used to allow business users to log in to various apps with a single password. Security Assertion Markup Language is used for the authorization while OAuth is used for the authentication process.
Is OAuth more secure than SAML?
Open Authentication, or OAuth, is another AuthN/AuthZ mechanism for safe authentication. In comparison to SAML, it is more focused on access scoping. Once an identity has been validated, access scoping is the practice of granting just the bare minimum of access to the resource/app that the identity requires.
SAML is meant to focus on corporate security, but OAuth is often not a viable solution for securing a company of hundreds or thousands of employees since it lacks encryption and relies on secure sockets layer/transport layer security (SSL/TLS) protocols for security.
Where is SSO used? SAML or OAuth?
Single Sign-On is possible with both SAML and OAuth, although their applications are vastly different. However, SAML is more user-specific, whereas OAuth is more application-specific. Both protocols approach it from different angles. The goal of SAML is to federate identities and eliminate the complexity of authentication. OAuth, on the other hand, allows a user who has previously been authenticated to delegate authority to another user. Each technique can be used as part of a larger authentication and authorization process, either in combination or in collaboration with other technologies.
Further Reading
Author



Leave a Comment