Need Help? We are right here!
Search Results:
×Privileged Access Management or PAM is an identity security solution that focuses on ensuring that only authorized individuals can perform critical tasks within an organization's IT environment. These tasks include installing software, making changes to system settings, or accessing sensitive data.
PAM framework is an identity security solution that focuses on managing and securing identities that possess elevated permissions beyond those of regular users. This encompasses a strategic blend of people, technology, and processes. PAM restricts access to key accounts and continuously monitors them. The domain of Privilege Access Management (PAM) falls within the broader scope of Identity and Access Management (IAM) and identity security. Fusing IAM with specific PAM controls ensures a robust defense against evolving threats targeting identity infrastructure, safeguarding the enterprise's most critical assets.
Privileged access refers to the special permissions granted to certain user accounts within an organization, allowing them to perform administrative-level tasks and access sensitive information beyond the reach of regular user accounts.
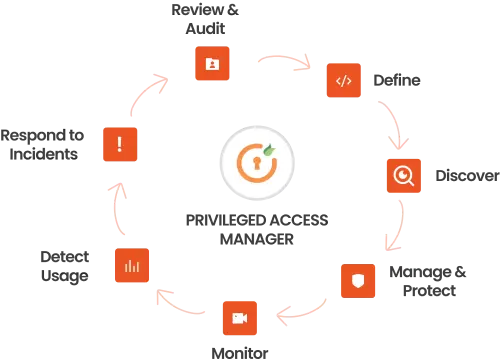
A privileged user is someone with special access to do important tasks that regular users can't. This might include IT staff, top executives, or others who need extra access.

Privileged Access Management (PAM) is a key security approach designed to protect your organization's sensitive data and systems. It grants and manages higher-level access for certain users, allowing them to perform important tasks across various accounts, systems, servers, and databases.
PAM ensures that only authorized personnel can access critical resources, reducing the risk of security breaches caused by compromised privileged accounts.

Key features of our PAM solution include:
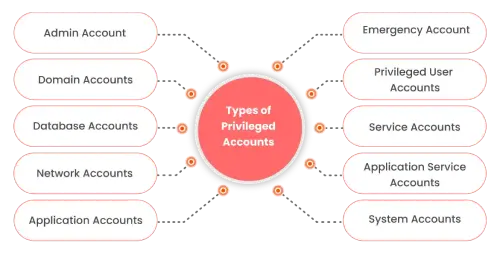
Privileged accounts are high-level enterprise accounts granting comprehensive access to critical IT tasks, distinct from regular user accounts by their advanced permissions. These accounts encompass human, application, and service accounts, each tailored for specific roles within an organization's infrastructure.Designed for IT professionals and administrators, privileged accounts enable full control over the system, network, and data management.
Understanding the variety of privileged accounts is key to safeguarding your organization's digital assets. While standard user accounts are sufficient for everyday tasks, certain roles within IT require elevated access for specialized functions.
Our platform separates these privileged accounts into distinct categories, each tailored for specific administrative and operational needs.


















Let us now have a look at some of the Privileged Access Management solutions offered by miniOrange
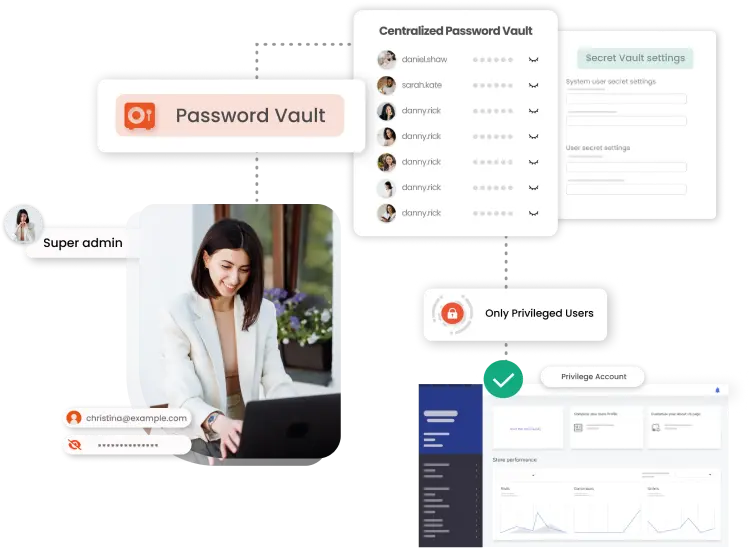
Protect your user accounts in a centralized manner with the Password Vault feature of miniOrange's Privileged Access Management solution. Implement strong passwords, and MFA, & regularly rotate & manage privileged account credentials with industry-standard encryption for secure password management.

Gain real-time visibility with live session streaming for prompt threat response through Session Monitoring & Control.
The Privileged Session Manager is a crucial component in managing secure access to an organization's sensitive IT assets.


The Privilege Elevation and Delegation feature of Privileged Access Management allows for the assignment of time-limited access to restricted resources for specific users, tailored to their current privilege levels.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Privileged Access refers to the dynamic provisioning of access rights to users for a limited duration, precisely when such access is required. It minimizes security risks associated with standing privileges.

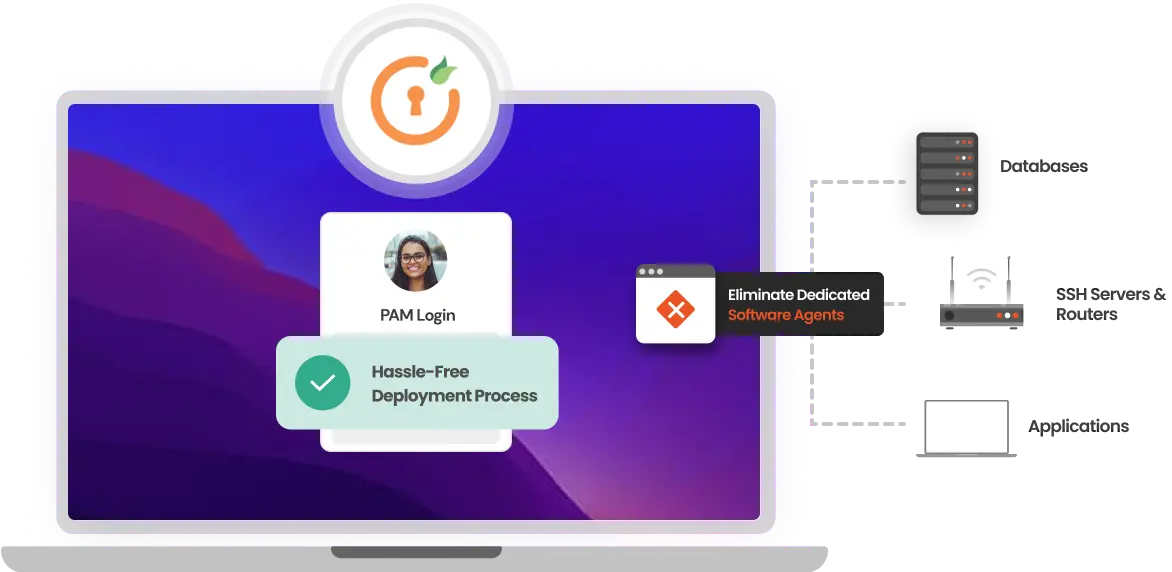
The Agentless Privileged Access Management feature offers a hassle-free deployment process, as it eliminates the need for installing and managing PAM agents on each endpoint.
The increasing number of endpoints and the growing complexity of cyber threats are making organizations more vulnerable than ever. Effective Endpoint Privilege Management is essential to protect sensitive data and Prevent unauthorized access. The Endpoint Privilege Management feature of miniOrange's Privileged Access Management solution enables you to:
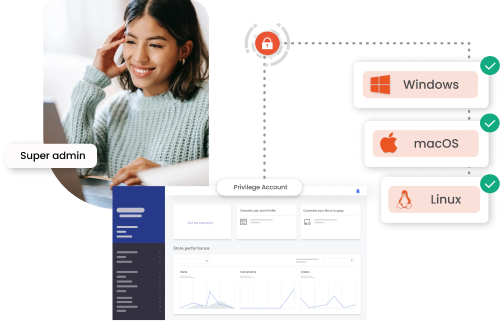
Privileged Access Management seamlessly integrates into your existing infrastructure, ensuring secure and
managed access to critical systems
Limits privileges, reducing entry points for threats and bolstering cyber defense.
Prevents malware installation and spread by enforcing of least privilege principles.
aligns privileges with job requirements, minimizing downtime and enhancing performance.
Streamlines compliance by restricting privileged activities, and meeting regulatory requirements.
Recognized by insurers for risk mitigation, facilitating easier coverage acquisition.
Enforces need-based access and monitoring, enhancing security against breaches.
Privileged Access Management (PAM) empowers security squads to pinpoint and respond to malicious user actions stemming from misuse of privileges. It facilitates prompt risk mitigation. By implementing a PAM strategy, organizations can guarantee that staff members possess just the essential access rights required for their roles. Beyond detecting malicious actions related to privilege misuse, a PAM system aids an organization to:
The more comprehensive your strategies and implementations are for privilege security, the more effectively you can respond to threats from both inside and outside your organization. In addition to fulfilling regulatory requirements. Let us now have a look at some of the key PAM best practices:
Identity and access management (IAM) comprises of a set of rules that identifies and controls the Who, When, Where, and How the user access to resources will be provided. These consist of Single Sign On (SSO), Multifactor Authentication (MFA), Password Management, and User Lifecycle Management.
The key difference between PAM vs IAM is that Privileged Access Management (PAM) involves specific processes and technologies dedicated to securing privileged accounts. PAM, as a critical subset of Identity and Access Management (IAM), is designed to regulate and monitor the actions of privileged users, who have access levels that surpass those of regular users once they are logged into the system.
When discussing the difference between PAM and PIM, it is important to note that Privileged Identity Management (PIM) is also a key component. It focuses on managing, monitoring, controlling, and securing the access rights of privileged users to critical resources within an organization.
Businesses can use Privileged Access Management to enhance their security by controlling, monitoring, and managing the access rights of users with elevated privileges. PAM helps reduce the risk of data breaches by ensuring that only authorized users have access to sensitive systems and information.
A Privileged Access Management (PAM) tool is a cybersecurity solution that helps organizations secure, control, manage, and monitor privileged access to critical digital assets. These tools are essential for enforcing security policies, providing secure authentication, and offering detailed logging information of all privileged sessions, thereby preventing unauthorized access and misuse of privileged credentials.
Privileged Access Management is needed to protect organizations from the risks associated with privileged accounts, such as insider threats, external attacks, and data breaches. By managing and monitoring privileged access, PAM solutions help ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive systems and data, this reduces the overall attack surface and enhances overall security.
The reason for granting high-privilege access to a user is to enable them to perform specific tasks that require elevated permissions, such as system maintenance, network configuration, or managing the security settings. High-privilege access is typically granted to the IT administrators and other roles that manage and secure the IT infrastructure.
Privileged Access Management tools should be administered by trusted professionals within an organization. These administrators are responsible for configuring the PAM solution, setting access policies, monitoring privileged user activities, and ensuring that the system remains secure against unauthorized access and potential security threats.
Privileged Access Management (PAM) in cybersecurity refers to the technology for managing control over the elevated privileged access and permissions that users have within an organization's IT environment. It is designed to prevent breaches and insider threats by managing and monitoring privileged accounts and their access rights.

Identity, Access, and Beyond