Need Help? We are right here!
Search Results:
×Privileged Account and Session Management (PASM) grants users temporary administrative access to critical corporate environments in an "all-or-nothing" manner. It is a specialized category within Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions. PASM solutions are designed to provide secure and traceable access to privileged accounts, ensuring that sensitive access remains both controlled and monitored.
Analysts at Gartner identified PASM as one of the primary solution groups in the PAM market in 2017, alongside Privilege Elevation and Delegation Management (PEDM).
There are two main key Components of PASM tools
Privileged Account Management (PAM) manages and controls access to privileged accounts—those with the authority to make critical changes within an organization's network. PAM solutions ensure that only authorized users can access these accounts, reducing the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive systems, data, and administrative functions. Through this, organizations can monitor and restrict who can unlock these high-level accounts, minimizing the potential for cyberattacks that take advantage of privileged access to move undetected within a network and cause significant damage.
Privileged Session Management (PSM): Facilitates the management, monitoring, and auditing of all sessions involving elevated access and permissions. This ensures advanced oversight and control, protecting the environment from insider threats and external attacks. It also provides critical forensic information required for audits and compliance with regulatory mandates.
Insider threats pose a significant risk. Without proper monitoring and management of privileged accounts, malicious insider activities can go undetected, increasing organizational risk. Key concerns include:
PASM solution is essential for meeting compliance requirements. Regulations like HIPAA and PCI DSS mandate the ability to audit the activities of privileged accounts. This auditing capability is crucial for compliance and avoiding penalties.
With PASM, organizations are better protected and compliant with industry standards as they continue to grow. PASM monitors PAM sessions to provide real-time oversight and control.
Password vaulting, or password management, securely stores and manages credentials in a centralized system. It promotes the use of strong, complex passwords, enhancing security within a privileged access management (PAM) framework.
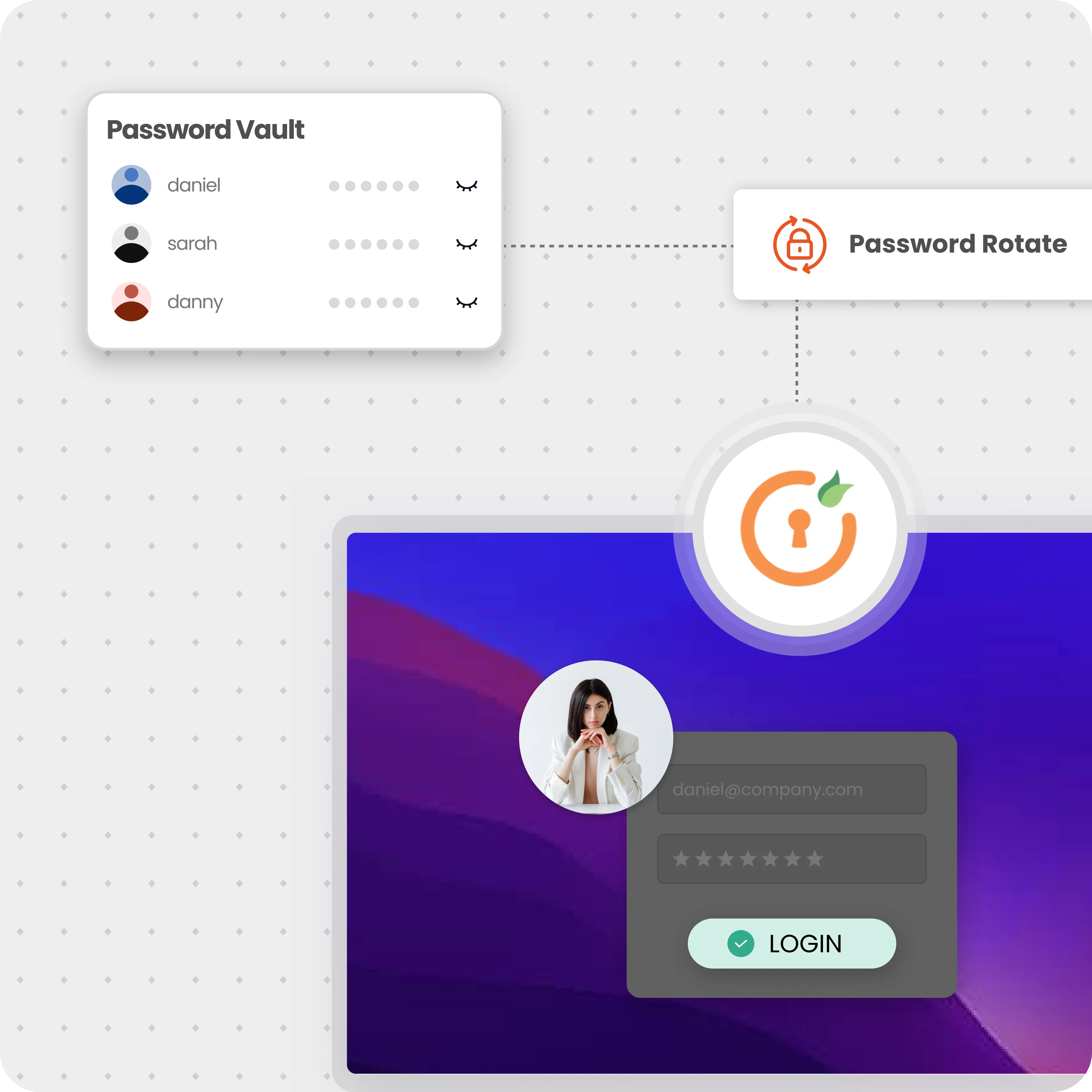
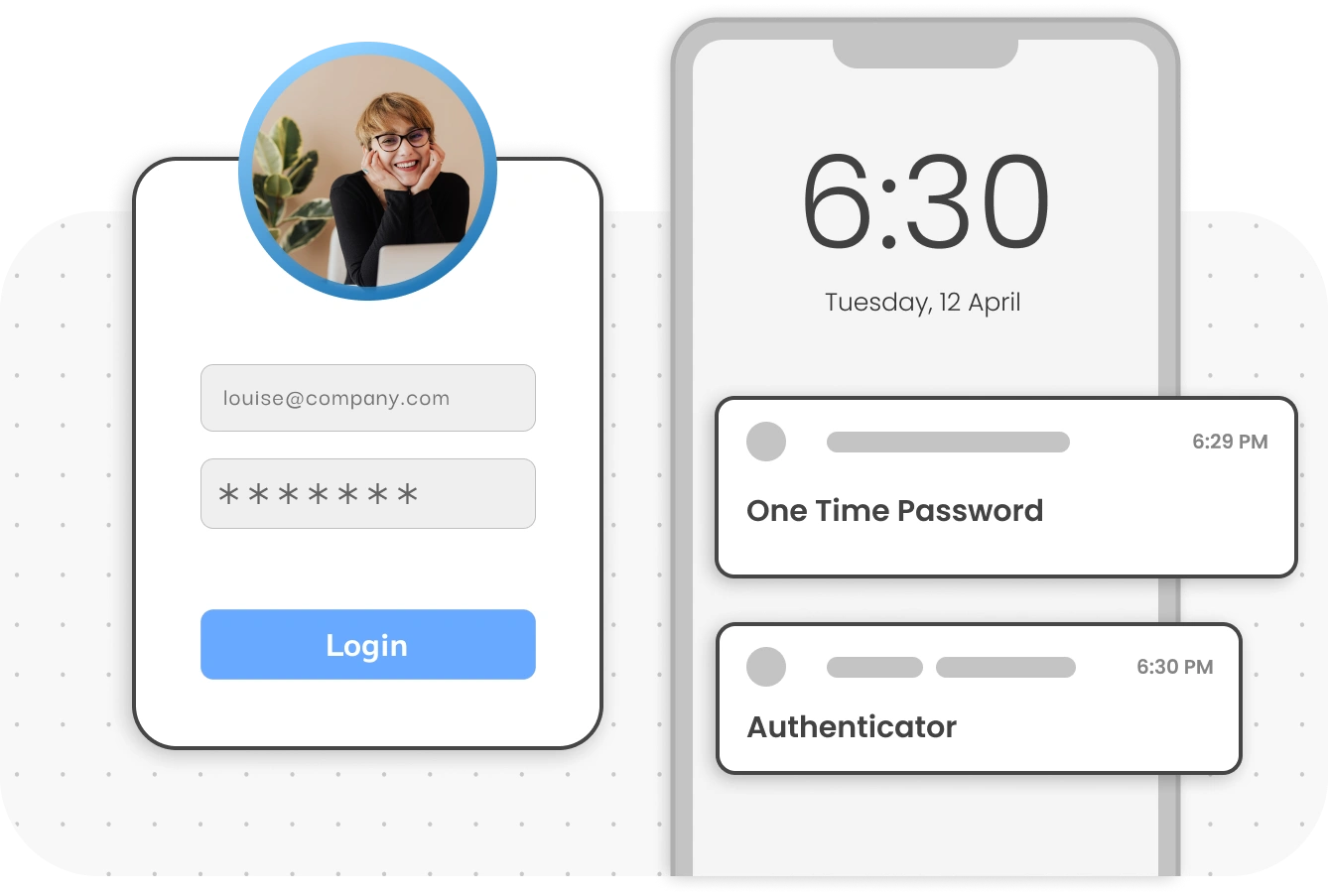
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires multiple verification factors for accessing enterprise resources and applications, whether on-premises or in the cloud. MFA secures all network devices and protects login access for Active Directory.
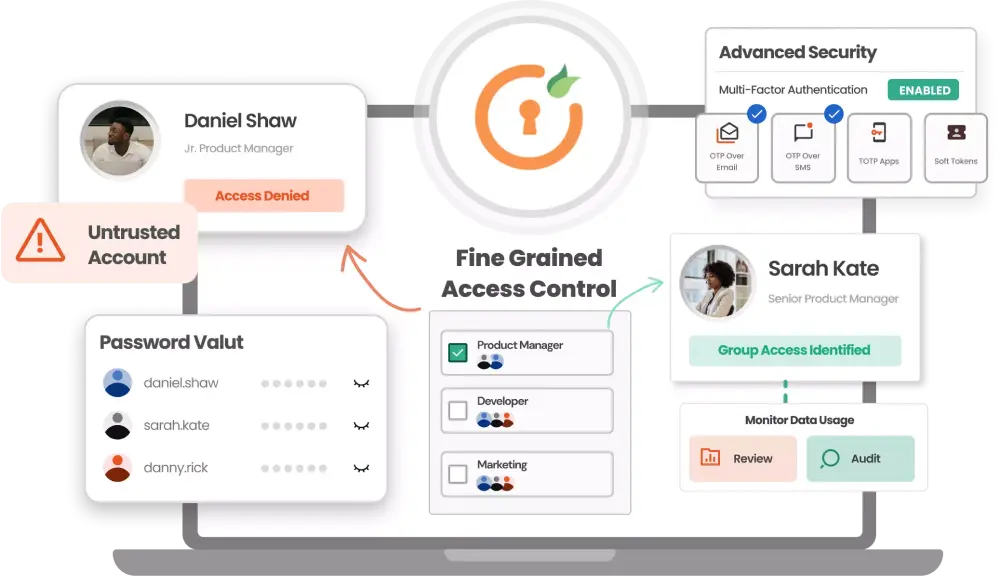
Offers enhanced oversight and accountability, it enables granular control over critical assets like databases and servers, minimizing misuse of privileges.

This feature enables users to securely access multiple cloud-based (SaaS) and on-premise applications with a single set of login credentials. It provides a unified dashboard for accessing all enterprise applications, integrates with any identity source like Azure AD, and allows admins to set custom rules for different user groups.
Privileged Account Management (PAM) secures and controls accounts with elevated access rights to sensitive systems within an organization. PAM solutions manage permissions, monitor activities, and audit access to ensure only authorized users perform critical tasks like system administration and configuration changes.
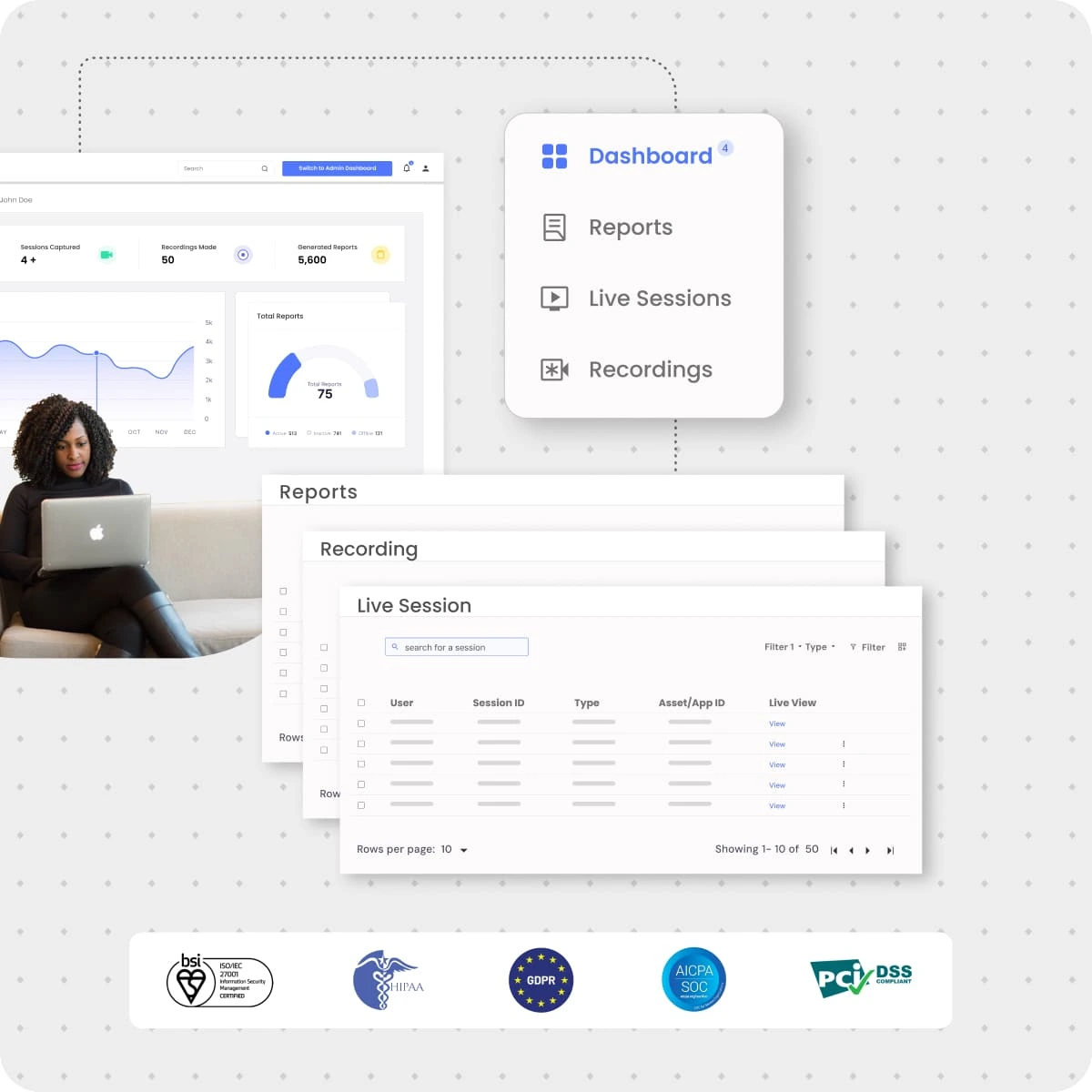
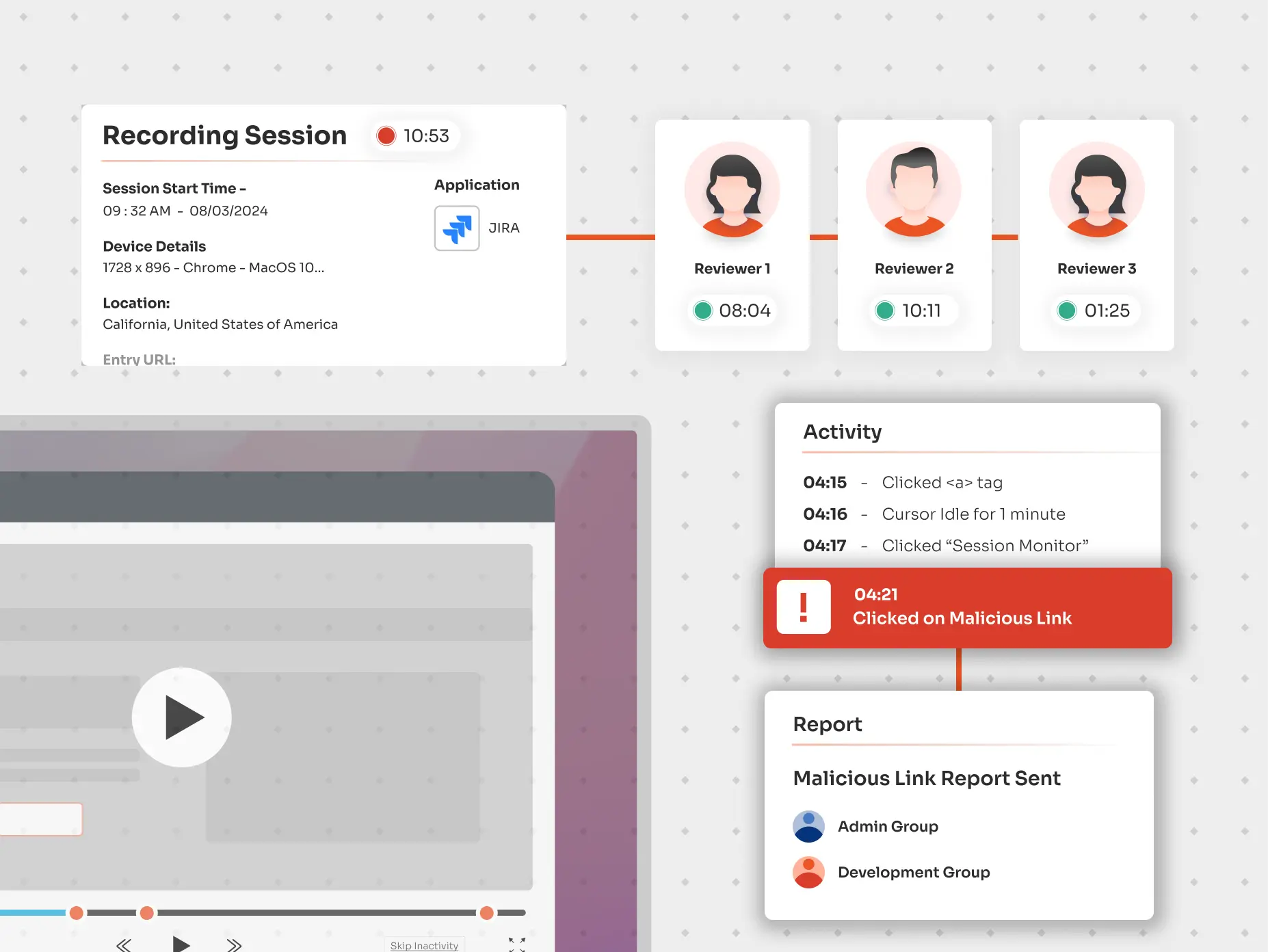
It protects business interests by monitoring and recording privileged user activities in real-time, automating logs, and tracking system errors, operational issues, or irregularities through comprehensive audit trails.
Discover and onboard privileged identities and credentials for all users and machines, ensuring complete coverage and security.
Manage and protect passwords, SSH keys, and DevOps secrets, keeping sensitive credentials secure and out of unauthorized hands.
Automatically inject credentials to start sessions, both on-premises and remote, while keeping them hidden from end-users for enhanced security.
Grant only the necessary access to users based on contextual factors, limiting access to what is needed for the shortest duration possible.
Monitor, audit, and manage all privileged sessions in real-time, with capabilities to pause or terminate sessions to maintain control over privileged activities.
Keep thorough records of privileged session activities, including playback options, for auditing, forensic analysis, and identifying any suspicious or unauthorized actions.
Privileged Account and Session Management (PASM) is a component of Privileged Access Management (PAM) that grants users administrative access to important accounts and sensitive systems, like data centers, databases, and applications, through remote sessions.
Zero Trust Architecture and Privileged Account and Session Management (PASM) are both security approaches aimed at minimizing risks within a network. Zero Trust Architecture operates on the principle of not trusting any entity by default, enforcing strict access controls. The PASM tool complements this by providing secure, controlled access to critical accounts and sensitive endpoints, ensuring that even privileged users are closely monitored and managed.
Together, they enhance security by ensuring that only authorized and authenticated users can access sensitive resources, and that their activities are tightly controlled and logged.
PASM tools grant users full administrative access for a limited period, with each session being carefully monitored and recorded for potential analysis. In contrast, PEDM (Privileged Elevation and Delegation Management) allows users to operate with their standard accounts, only providing the necessary access privileges. As a result, PEDM requires less monitoring and recording compared to PASM.
In cybersecurity, Privileged Session Management (PSM) is a component of Privileged Access Management (PAM) that focuses on securing, managing, and monitoring privileged sessions to ensure that high-risk activities are controlled and tracked effectively.
PASM (Privileged Account and Session Management) enhances your overall PAM (Privileged Access Management) strategy by providing secure, controlled access to critical accounts and sensitive endpoints.
It ensures that privileged sessions are carefully monitored and recorded, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and helping to maintain compliance with security policies. By managing and securing these high-level accounts, PASM strengthens the overall security posture of your organization.
Common Threats Mitigated by PASM:

Our Other Identity & Access Management Products