Need Help? We are right here!
Search Results:
×Granular access control means giving specific permissions to users or groups, allowing them access to the resources or data they need, and nothing more.
Granular access control aka granular security mechanism enables a business to manage and restrict access levels of their data and resources, in a highly detailed way. Rather than giving complete access to users, it breaks down permissions into specific actions or objectives, ensuring users only have the access they need and no more.
Granular access control is an important component under Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Privileged Access Management (PAM). In simple terms, granular access control acts as a safety net. It separates those who can see or modify data from those who can carry out tasks. This strengthens security and clearly defines roles within an organization or system.
Additionally, through role-based capabilities, PAM limits actions users can undertake on remote applications, including SSH, RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol), and database systems. This strategy effectively reduces standing privileges, ensuring users can only execute operations specifically provisioned to them.







A centralized platform manages credentials, limits access, tracks data, and maintains logs, reducing breach risks and enhancing security.
Enables fine-tuned access rights for users or groups, with custom restrictions on sensitive data based on roles and job functions.
Facilitates detailed documentation and audit trails, ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR.
Command restriction controls what commands users can run. This is crucial for preventing unauthorized access or misuse of sensitive commands.
For example, administrators can block specific commands in PowerShell or Command Prompt (CMD) to stop users from running high-risk actions.
Query restriction limits the types of database queries users can execute. For instance, you can allow users to only view data without the ability to change it.
Use SQL permissions or Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to control who can run which types of queries.
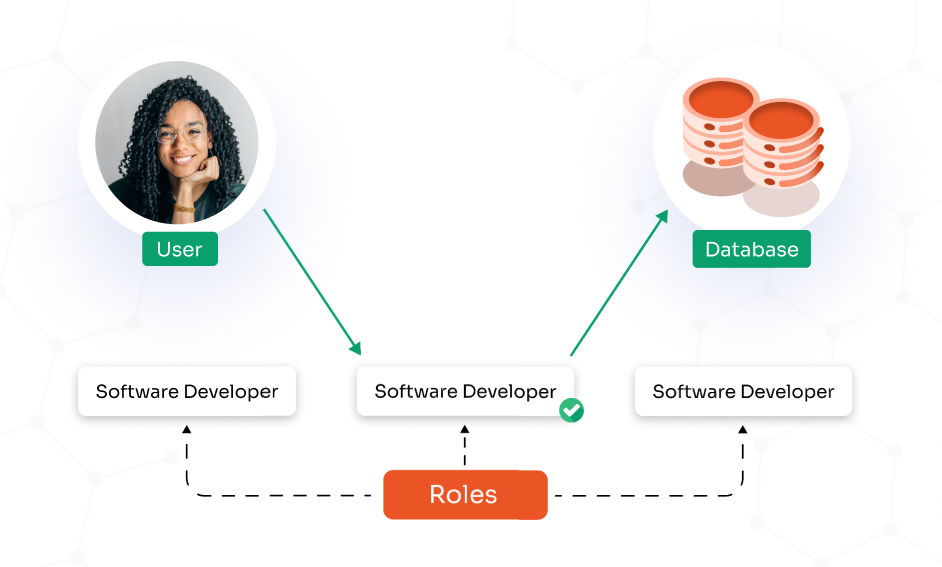
Roles define what users or services can do, and capabilities are the specific actions allowed for each role. This approach is known as Role-Based Access Control (RBAC).
App restrictions prevent users from running unauthorized applications when accessing a system remotely, whether through RDP, SSH or VNC.
When determining the specific security requirements for granular permissions within your organization, you have several options to consider
RBAC is based on granular access control that limits access based on the user’s role in an organization, where every role has specific permissions associated with it. Instead of assigning permissions to each user, they are assigned to a role, that defines their level of access.
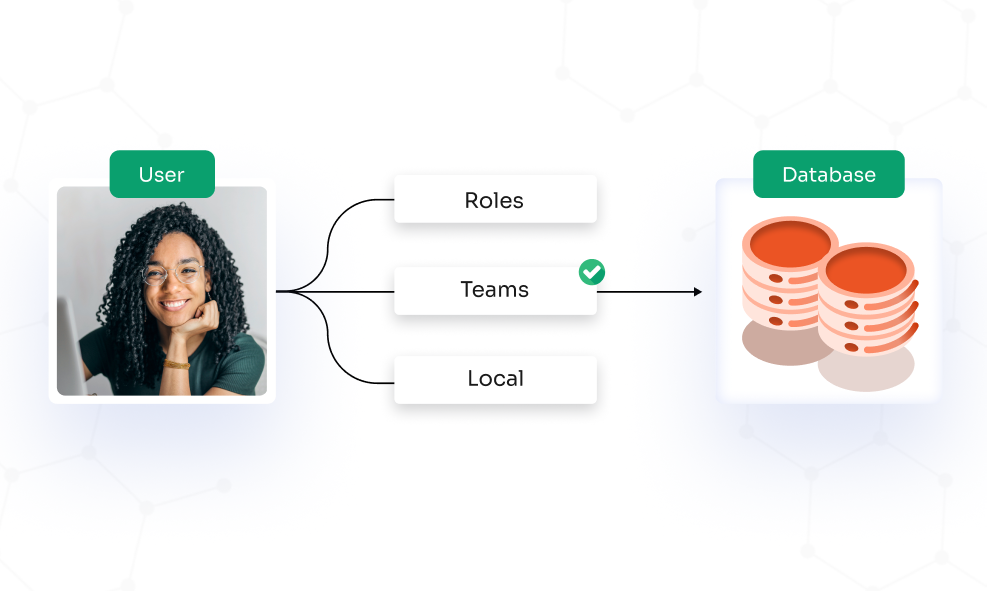
Access control is defined by user attributes like user role, time, rank, location, etc. Access to data and resources is granted based on the combination of these attributes.
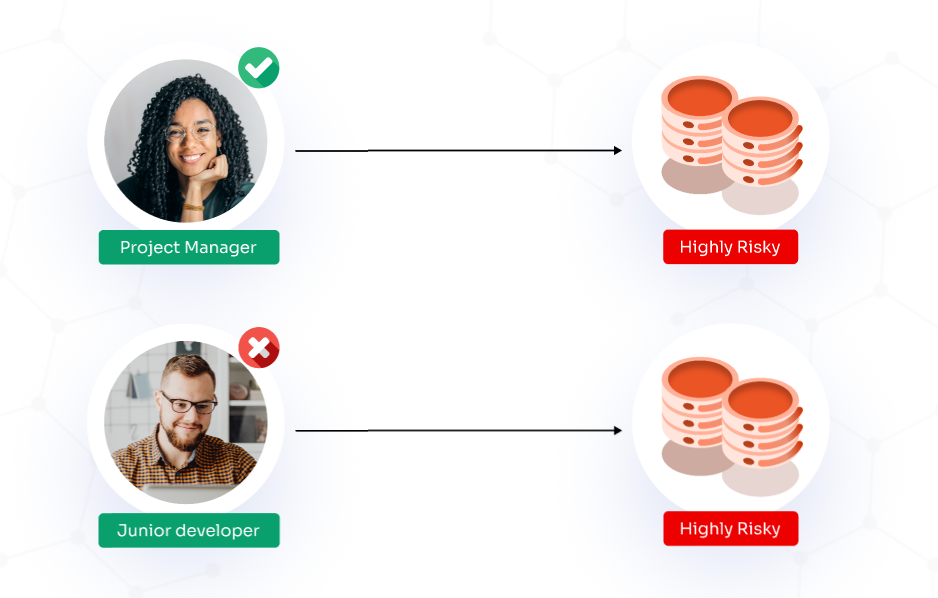
In an MBAC system, the administrator implements controls specifically for high-security environments. Access is granted or denied based on the sensitivity of the information within the resources and the user’s security clearance level, such as confidential or top secret.
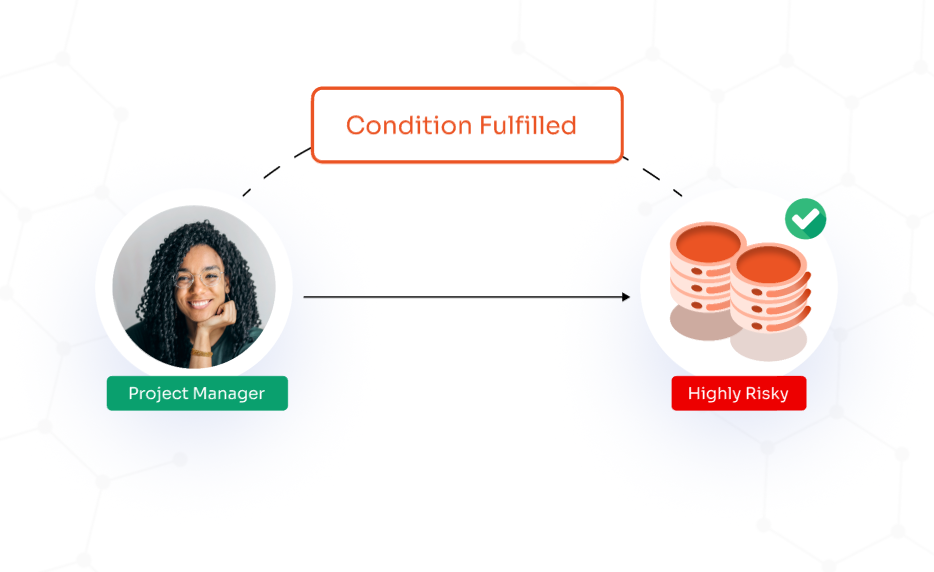
DBAC allows users to manage access to their resources, enabling them to decide who can access their data & under what conditions. Users have the option to set access rights and set the conditions for this access as it can introduce security risks if permissions are not carefully maintained.
Access control is a security technique that regulates who can view or use resources in an organization. It ensures that only authorized users, systems, or processes have access to specific resources, such as files, databases, and other critical assets. Access control determines the permissions of users and systems, which might include the ability to read, write, or modify data.
Mandatory Access Control (MAC), Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Discretionary Access Control (DAC), and Rule-Based Access Control (RBAC) are the four main types of access control used to secure resources.
Granular permission control refers to the ability to specify detailed and precise access rights for different users or groups. It allows system administrators to restrict access in a way that only specific users or groups can access certain tables of data in databases. This ensures that individuals have access only to the information they need for their roles.
Granular access works by allowing administrators to define who can have access to each part of a system, as well as what they can do with that access. This means permissions can be finely tuned so that each user or group only has the access necessary for their specific tasks. This detailed control helps to ensure security and operational efficiency by limiting access to sensitive areas and functions within a system.
The Six Ws of Granular Access Control
Granular roles and permissions involve setting up a finely tuned system of access control within an organization. This system specifically creates four levels of access that a user or a folder can have on a document, ranging from basic viewing to full administrative rights like editing or deleting.
Granularity in security refers to the detailed and precise control over access within a system. This concept allows administrators to define who can have access to each part of a system, as well as what they can do with that access. Granularity ensures that permissions are customized to the needs of the organization.
Granular control access can be configured for controlling access to data, managing applications, overseeing network resources, adjusting system settings, handling privileged access, governing cloud services, and regulating Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Role Based Access Control (RBAC) is the most granular type of access control.

Our Other Identity & Access Management Products