Need Help? We are right here!
Search Results:
×
Privileged password management, is a critical feature of Privileged Access Management (PAM). It is a system designed to securely manage and protect privileged credentials. These privileged passwords provide elevated access and permissions within an organization's applications and systems.
Privileged password management automates credential discovery, access control, secure storage, and password rotation while offering alerting, reporting, and oversight for full monitoring of privileged credentials. Also known as enterprise password management or password vaults, it enhances security and compliance by efficiently managing sensitive credentials.
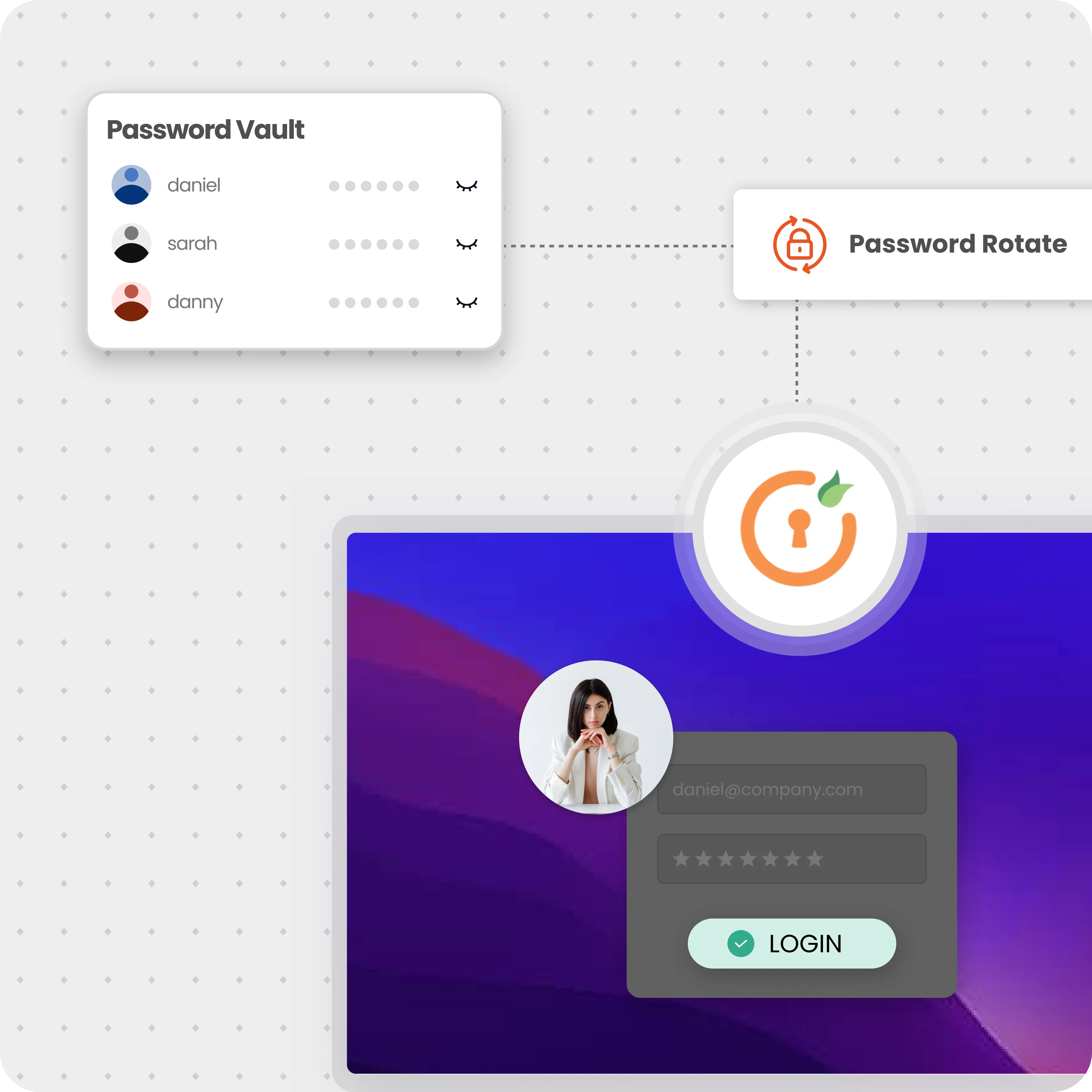
Privileged passwords are used to access accounts with elevated privileges, such as root, administrator, and service accounts. A privileged password management tool securely stores these passwords and grants access only to authorized users.
Here's a typical flow of how privileged passwords work:
Enterprise password management is essential for securing privileged accounts across an organization.
Without privileged password management software, organizations lack visibility and control over privileged accounts, increasing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. Enterprise password management tools provide centralized management, ensuring all privileged credentials are securely stored, monitored, and rotated.
Managing passwords manually is inefficient and prone to errors. Enterprise password management automates crucial tasks like password rotation, access control, and auditing, reducing the workload on IT teams and enhancing security.
Privileged password manager for enterprises ensures that organizations meet compliance requirements by maintaining detailed logs and reports. It mitigates risks by securing not just human but also non-human credentials, such as those used by applications and services.
Simplifies the creation of strong, unique passwords by generating secure credentials with customizable length and complexity.
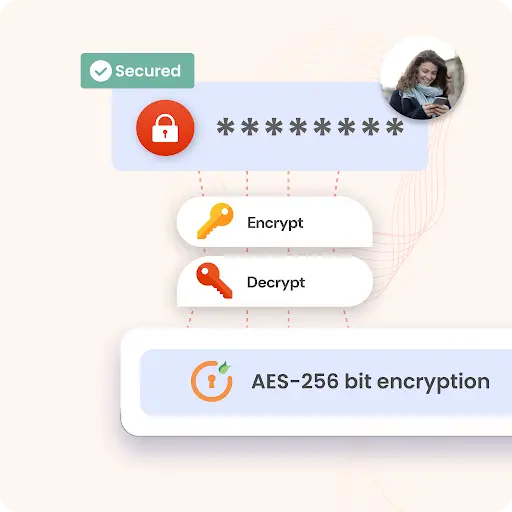
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES): A widely adopted symmetric block cipher selected by the U.S. government to protect classified information.
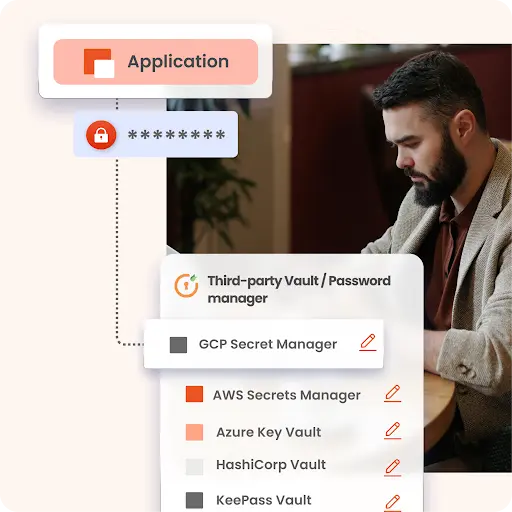
Seamlessly integrate with a wide range of password managers and vaults supported by miniOrange
Such as; GCP Secret Manager, AWS Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault, HashiCorp Vault, KeePass Vault, and any other third-party vault or manager.
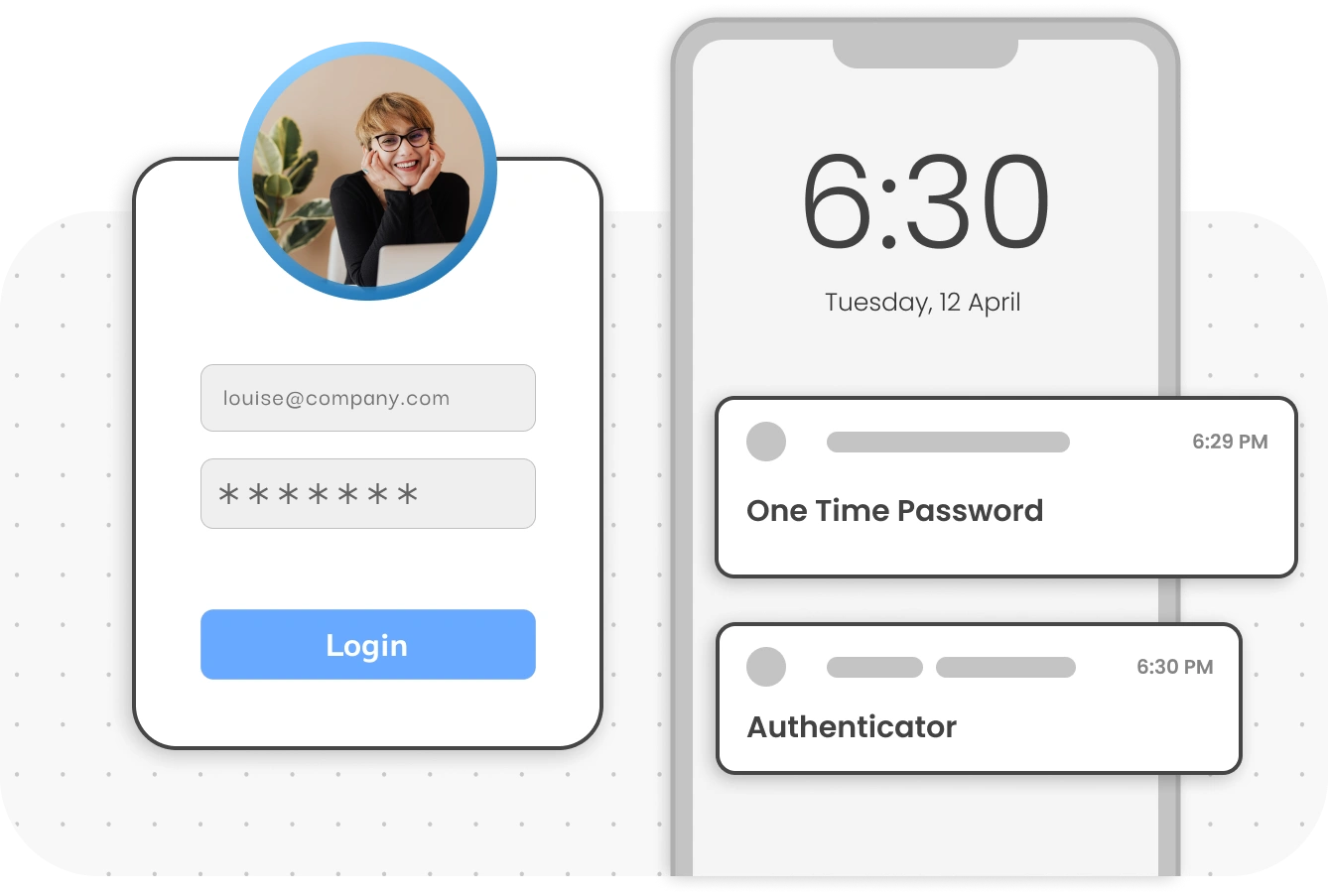
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): boosts security by pairing a password with an additional verification method:
A specialized device designed to securely manage and protect cryptographic keys throughout their lifecycle. HSMs act as trust anchors, ensuring that sensitive keys are stored and processed within a tamper-resistant environment.

Privileged password management safeguards sensitive information and prevents unauthorized access, reducing the risk of compromised accounts and data breaches.
Password generation, secure storage, and autofill simplify password management, minimizing disruptions and improving access to systems and applications.

By securely storing privileged passwords, organizations ensure quick and centralized access to critical resources, maintaining operational continuity without delays.
Password management software is needed to securely store and manage all your passwords in one place. It allows you to use strong, unique passwords for every account without the need to remember each one. This reduces the risk of security breaches associated with using the same password across multiple accounts and makes accessing your accounts quicker and easier by auto-filling login details.
Privileged password management best practices are essential for securing sensitive accounts and controlling access. Key practices include:
These best practices help enhance security and reduce the risks associated with privileged accounts.
Password requirements for a privileged account is to use a strong, unique password that is at least 12-16 characters long, with a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid common words, and personal information, and reuse passwords across different accounts.
Passwords should be regularly rotated, typically every 30 to 90 days, and always paired with multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security. These measures help ensure the integrity and security of privileged accounts.
Privileged password management focuses on securing and controlling access to privileged accounts with elevated permissions, using stricter controls like password rotation, auditing, and access restrictions. In contrast, password management is more general, dealing with the secure storage, generation, and management of passwords for standard user accounts.
The key difference lies in the level of security and control required for privileged accounts compared to regular user accounts.

Our Other Identity & Access Management Products