Need Help? We are right here!
Search Results:
×Privilege Elevation and Delegation Management (PEDM) means, granting users temporary access to higher-level privileges or delegating specific tasks while maintaining security and adhering to the principle of least privilege (PoLP).
Elevated privilege is the key feature of PEDM. Unlike permanent privileges, this elevation management approach allows access only to authorized areas for a designated time, enhancing security by limiting unnecessary control. PEDM, part of the broader Privileged Access Management (PAM) framework, provides more granular control compared to traditional Privilege Account and Session Management (PASM) technologies, thus preventing excessive permissions and bolstering IT security.







PEDM (Privilege Elevation and Delegation Management) operates by providing time-limited access to sensitive data or systems based on validated needs, effectively ending the risk associated with permanent standing privileges.
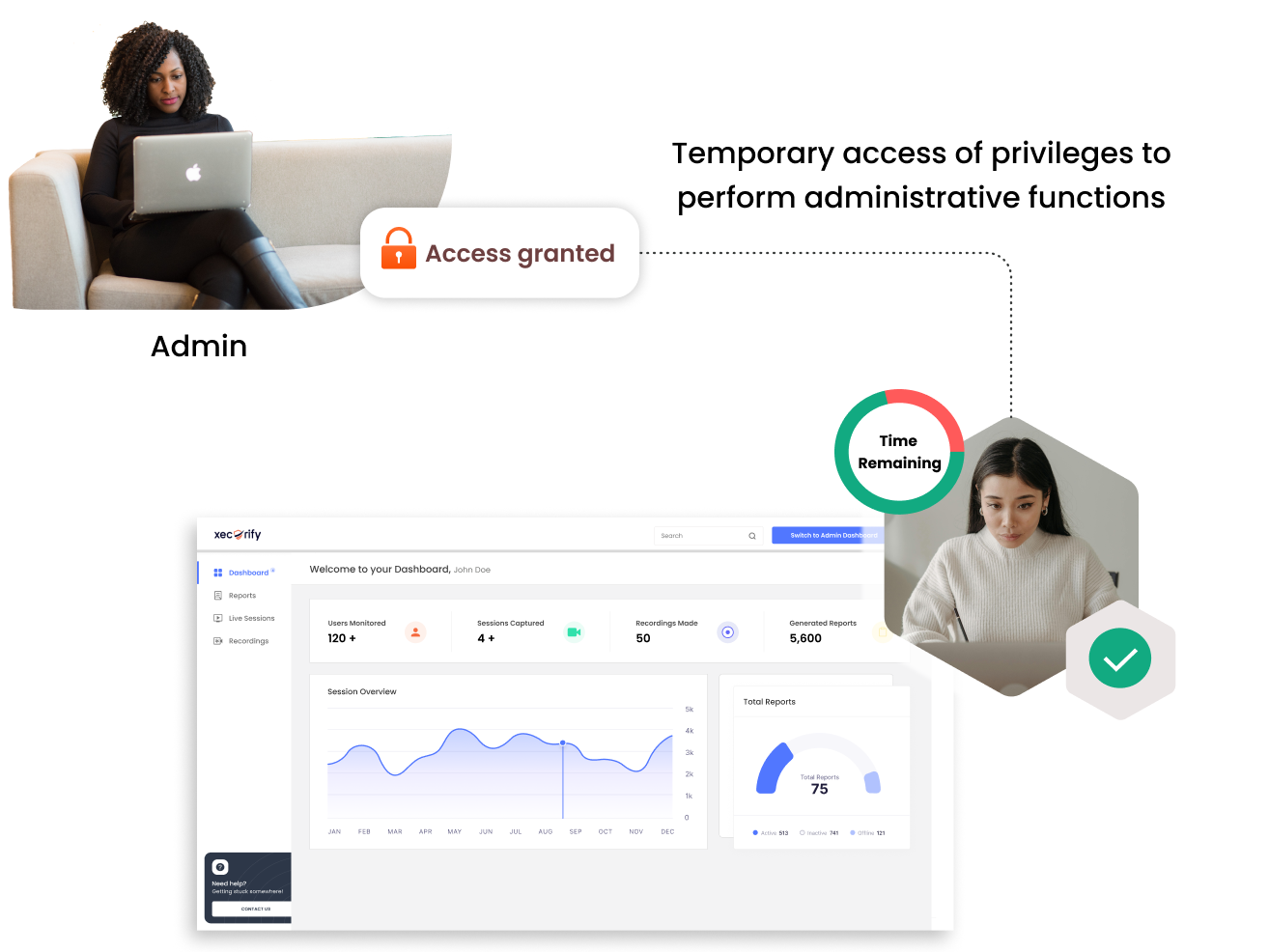
When users require elevated privileges to access critical systems, they submit a request to administrators. This request is carefully reviewed, and if considered necessary, elevation privileges are granted temporarily. This process is part of what is known as just-in-time privileged access management (JIT PAM), ensuring that privileges are granted just when needed and are closely monitored.
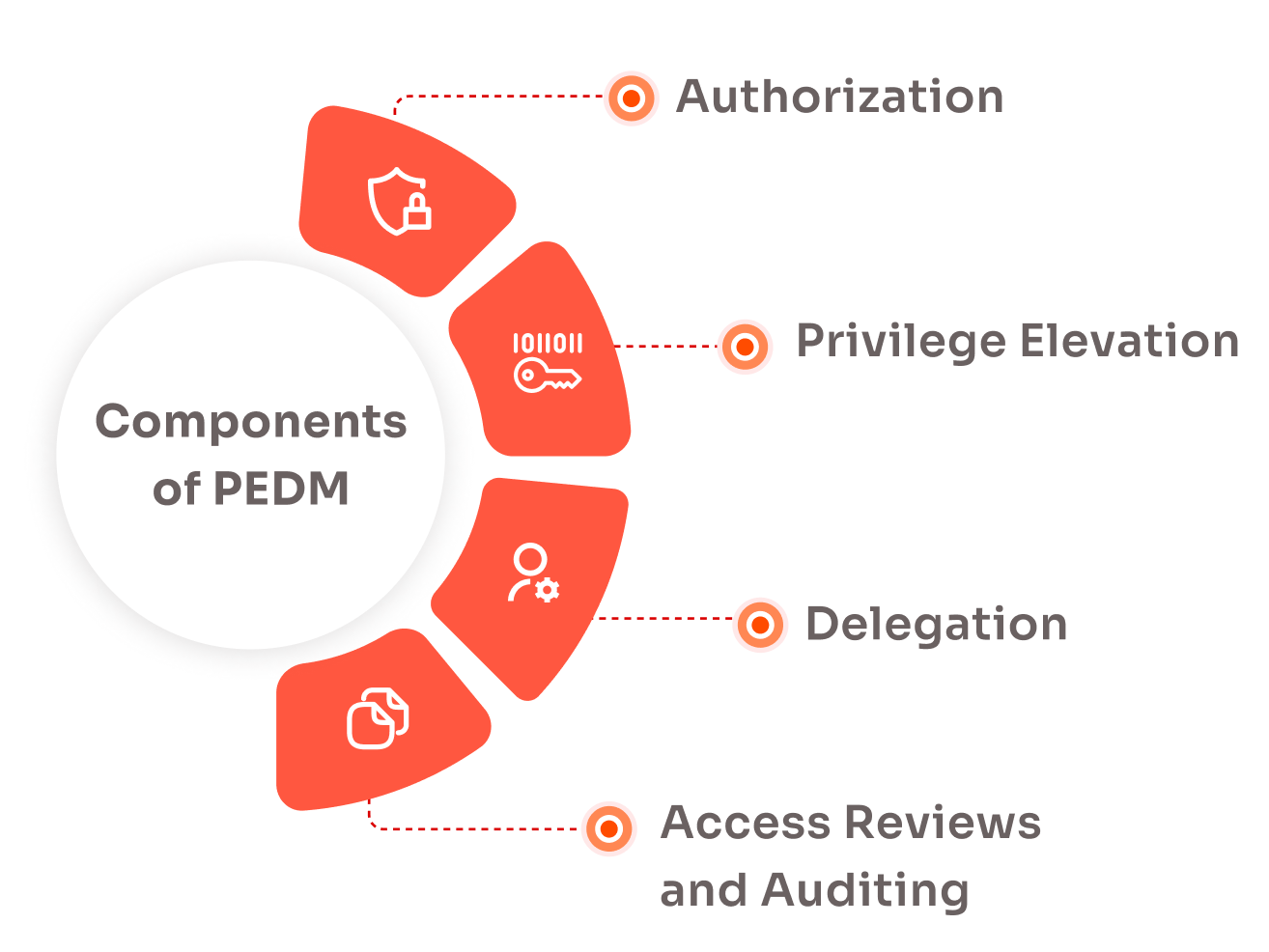
PEDM integrates seamlessly into a broader Privileged Access Management (PAM) framework and involves several key components
Technologies for privilege elevation and delegation management fall into two main categories:
The relationship between PEDM (Privilege Elevation and Delegation Management) and PASM (Privileged Account and Session Management) can be understood by recognizing how they each address different aspects of Privileged Access Management (PAM). As defined by Gartner in 2017, the PAM market is bifurcated into these two categories, each serving unique but complementary functions in managing privileged accounts.

This structured approach delineates how each component of the PAM strategy plays a crucial role, working together to provide robust and secure privileged access management.
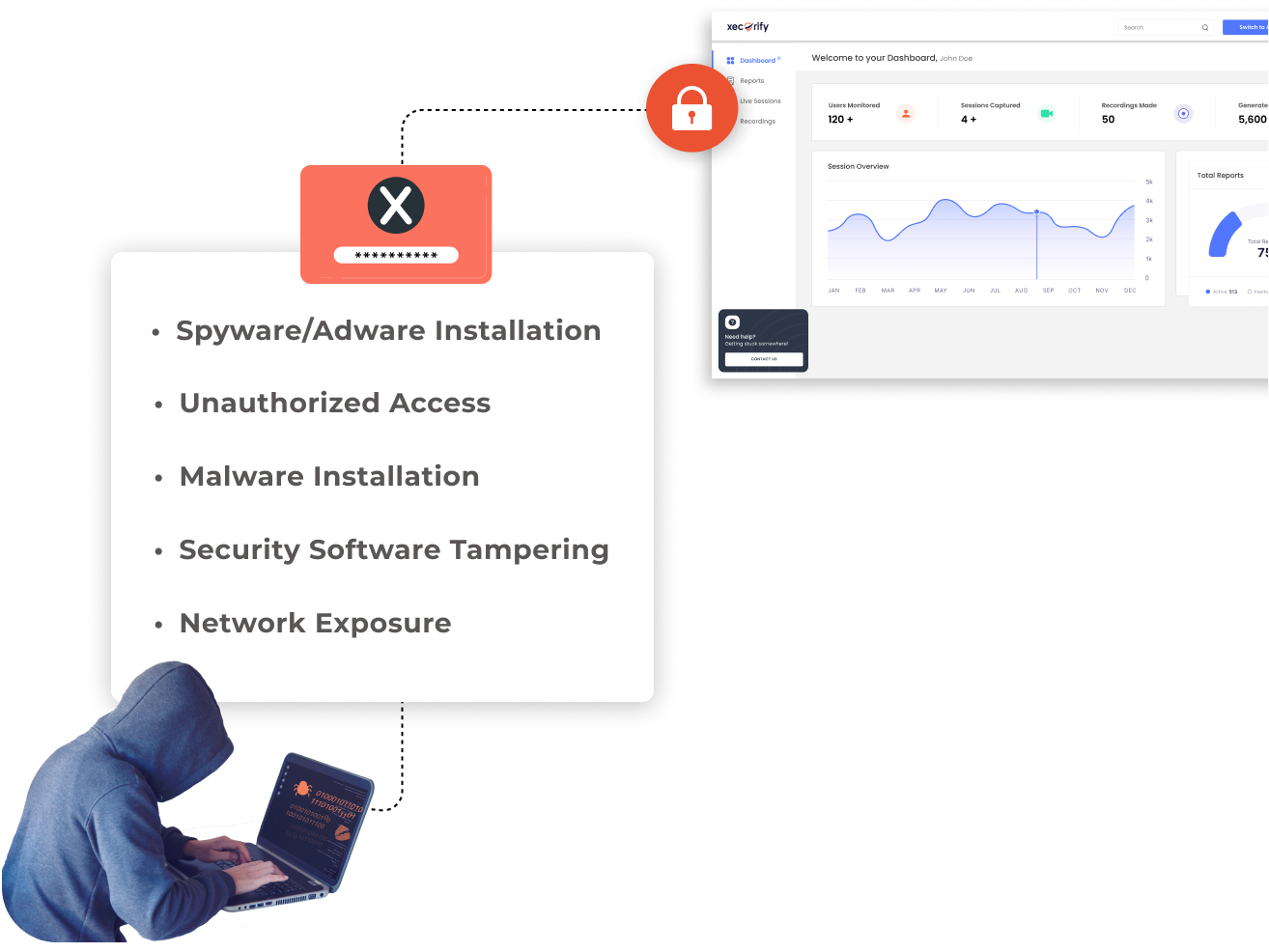
PEDM (Privilege Elevation and Delegation Management) plays a crucial role in mitigating a variety of cybersecurity threats by controlling access to resources on a need-to-know basis and minimizing unnecessary privileges. Here are some examples of threats that PEDM helps mitigate:
Through the granular control of user privileges and access rights, PEDM effectively limits the potential for these and other security threats, enhancing the overall security posture of an organization.
Privilege Elevation and Delegation Management (PEDM) plays a critical role in safeguarding an organization's IT environment, let us understand how
Let us now have a look at some of the core Features and capabilities of Privilege Elevation and Delegation Management (PEDM)
In PEDM:
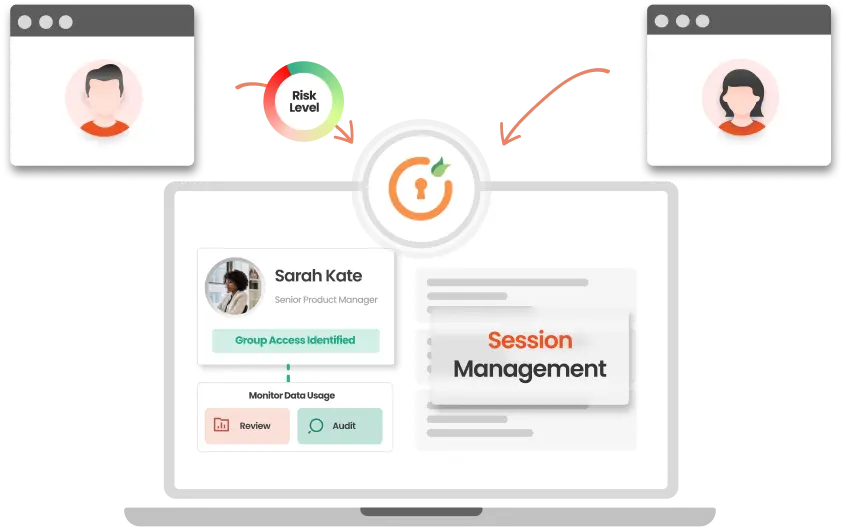
PEDM effectively manages and controls access by:
PEDM employs a strategic approach where:

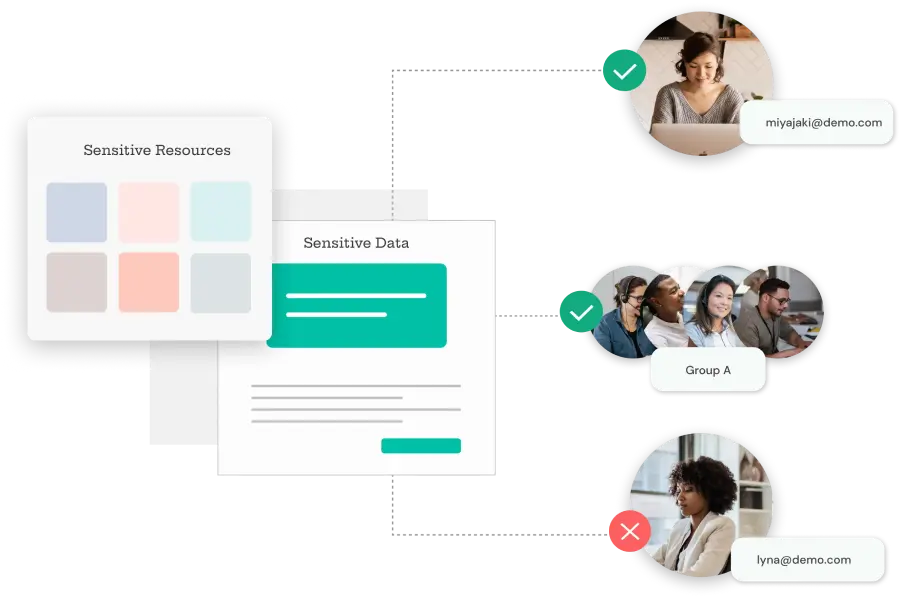
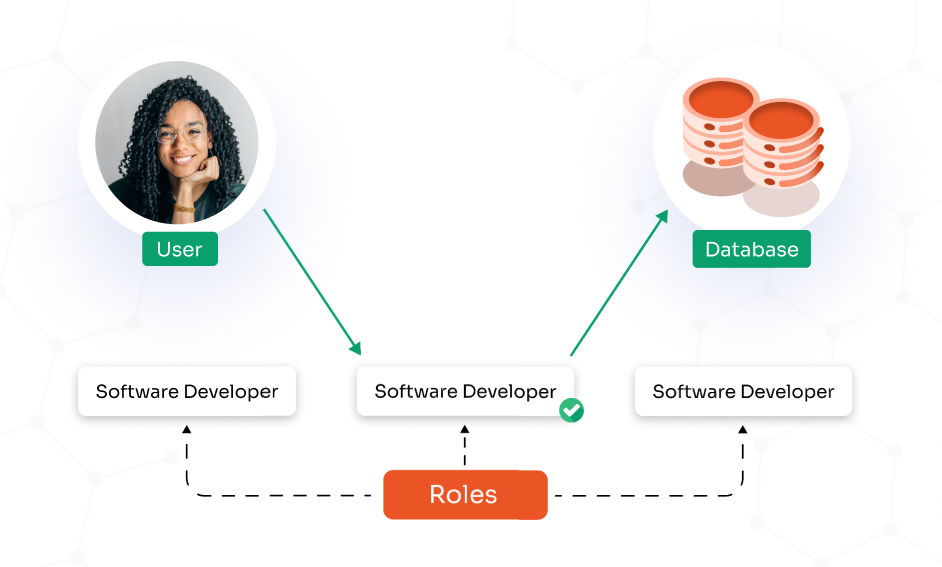
PEDM provides granular control over privileges:
PEDM employs a strategic approach where:

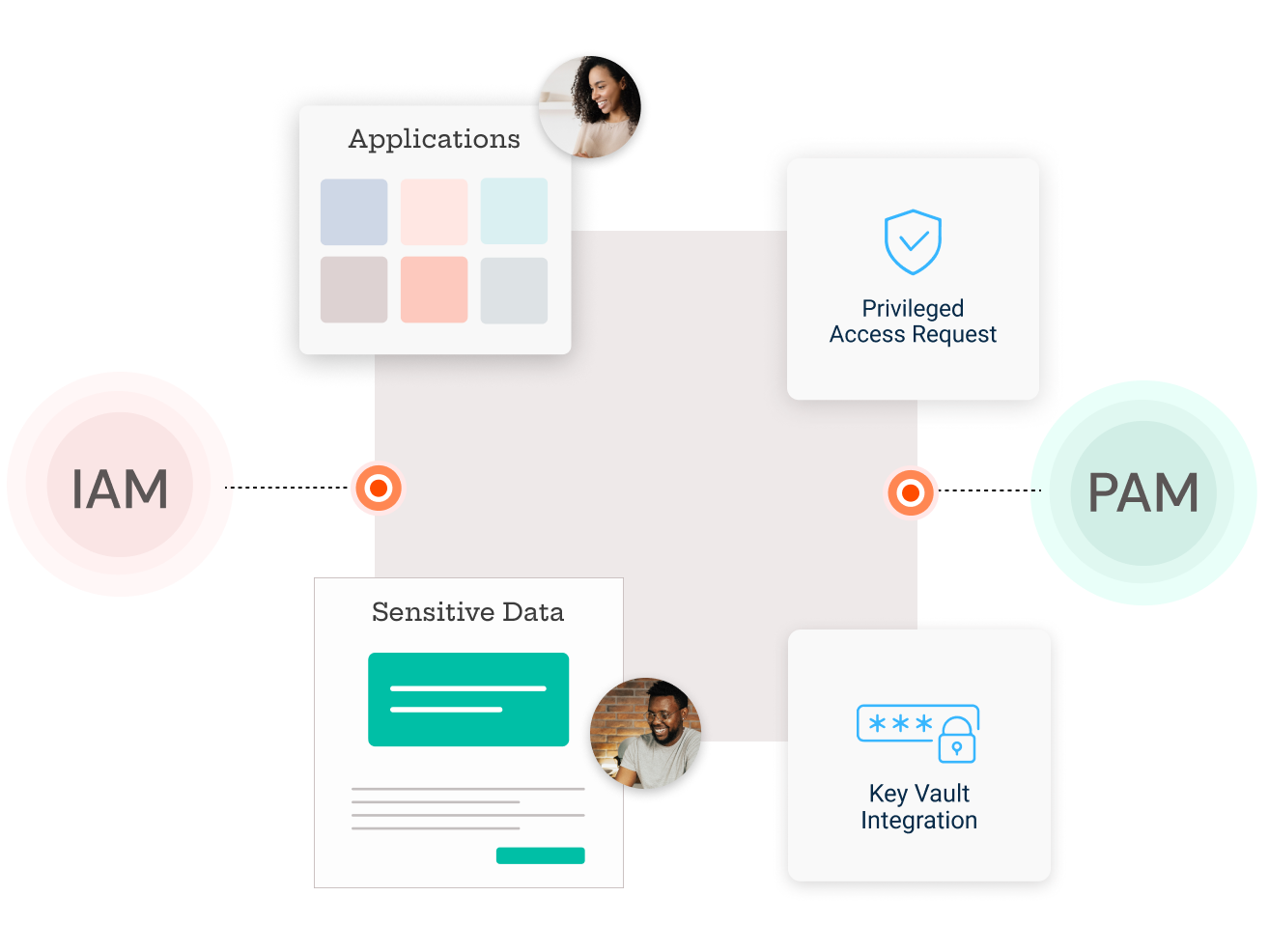
PEDM integrates seamlessly with existing IAM frameworks:
Our solution strengthens system security by separating privileges, giving temporary admins only the access they need. This reduces unauthorized access and adjusts privileges based on conditions.
Users can request temporary access with automatic approval based on set criteria, ensuring compliance and reducing admin work.
Elevation requests are quickly validated and approved, ensuring timely access without compromising security.
Privileged Access Management seamlessly integrates into your existing infrastructure, ensuring secure and
managed access to critical systems

I can't speak highly enough regarding miniOrange, I am totally satisfied with the process and results in every regard.
5.0

Awesome tech service, Awesome product. Overall Awesome people. This solution is very simple and easy to implement
5.0
Implementing a Privilege Elevation and Delegation Management (PEDM) strategy involves:

Our Other Identity & Access Management Products