Need Help? We are right here!
Search Results:
×Password rotation is a cybersecurity practice where passwords and privileged credentials (such as tokens or certificates) are regularly changed or reset to reduce the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive systems and data.
By periodically updating credentials, organizations can better protect against security threats and ensure that only authorized users have access to critical information. Regularly changing passwords reduces the risk of theft or misuse. IT systems often enforce policies requiring users to update passwords at set intervals, like every 30, 60, or 90 days. When you change your password, the system ensures it meets certain rules for strength and uniqueness, limiting the time a compromised password can be used. Think of it as updating the security code on your home alarm system to keep intruders out.







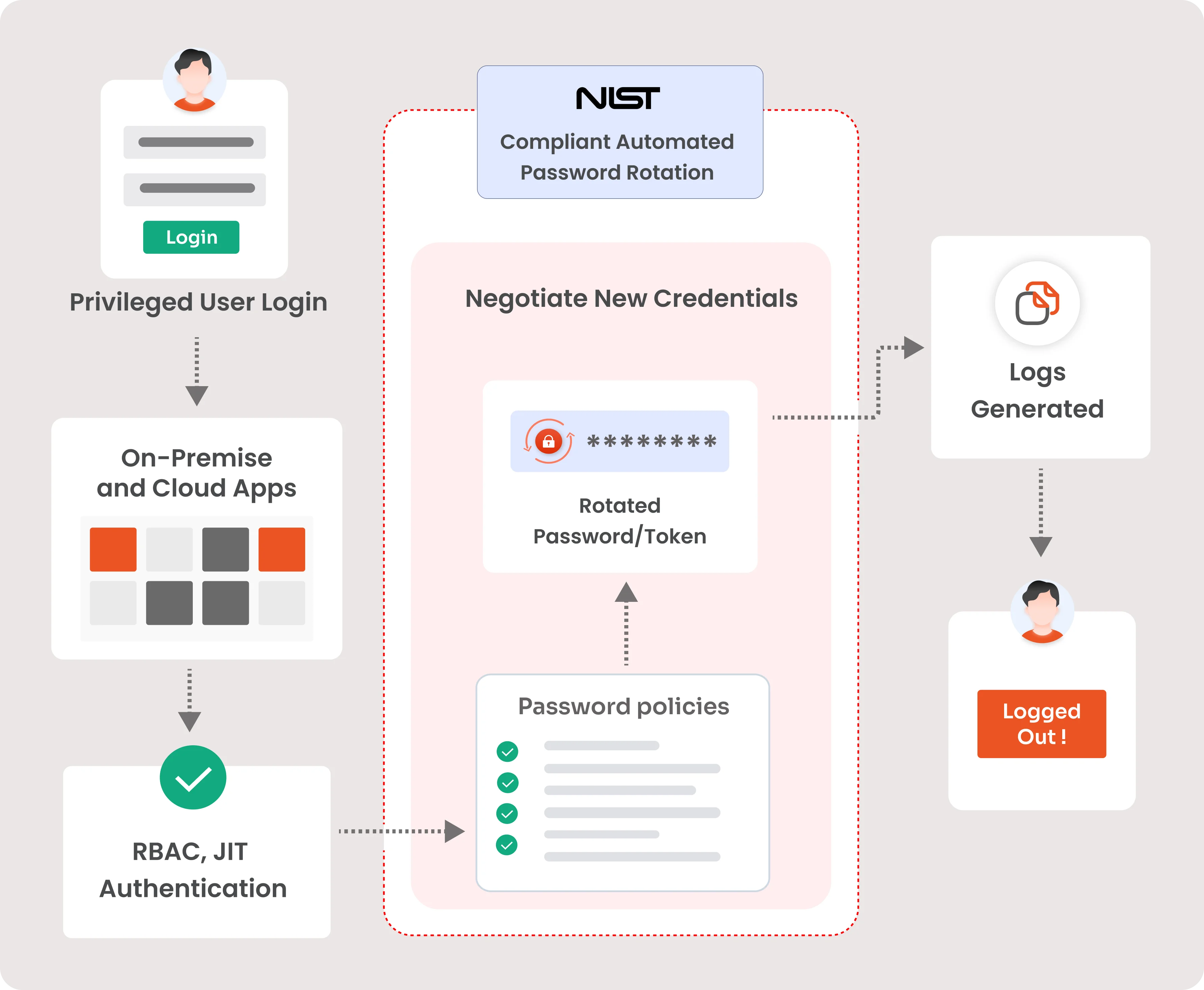
miniOrange password rotation in PAM offers password rotation at system level. For instance, to protect the endpoints, we offer RDP, SSH and VNC. Also, for servers, we offer system level password auto-rotation for AD and DB. Here is a simple workflow of how it is executed:
Security administrators create password policies to ensure passwords are complex and unique. Automated password rotation enforces these policies across all accounts, making sure every password meets the standards. This helps maintain strong security by preventing weak or easily guessable passwords.
The system continuously monitors password usage through authentication logs or real-time monitoring. As soon as a password is used, the password automation engine triggers an immediate password change or as per the preset intervals defined in the policy. This proactive approach ensures that passwords are rotated frequently, reducing the risk of unauthorized access due to compromised credentials.
Once a password change is triggered, the automated password rotation generates or negotiates a new, compliant password, certificate or token. This new password is then updated in directory services, such as Active Directory or LDAP, ensuring that all systems recognize the new credentials. Additionally, the new password is securely stored in an encrypted Password Vault, safeguarding it from unauthorized access.
Users are promptly notified of the password change and provided with instructions to retrieve the new password. All actions, including password generation, update, and storage, are meticulously logged with timestamps and user IDs. The Compliance Module generates reports demonstrating adherence to NIST standards, which are used for internal and external audits to ensure compliance. This comprehensive approach not only enhances security but also ensures regulatory compliance.
Boost Security with miniOrange: Auto-Rotation, Scheduling, Password Vault, Management & Compliance
Automatically rotates passwords and certificates after each use, if set, for various protocols and user types such as SSH, RDP, VNC, AD, DB, and system users, ensuring that credentials are always fresh and reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Allows password changes at predefined intervals (e.g., 30, 60, or 90 days) or custom schedules based on security levels, providing flexibility to meet different organizational needs.
Ensures the last 10 passwords are not reused to maintain password integrity, thereby preventing potential security breaches from recycled credentials.
Supports miniOrange’s Password Vault and third-party vault integrations (such as GCP Secret Manager, AWS Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault, HashiCorp Vault, and KeePass Vault) for robust password governance and centralized management.
Provides detailed audit trails and reporting to ensure compliance with standards like PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR, helping organizations meet regulatory requirements and maintain security best practices.
Passwords should be between 8-64 characters to ensure adequate security.
Allow the use of non-standard characters to increase password complexity.
Encourage the use of long passphrases for better memorability and security.
Passwords should only be reset if they are compromised or forgotten to avoid unnecessary changes.
Strongly encourage the use of multi-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security.
Ensure passwords are stored securely using strong hashing algorithms to protect them from breaches.
Password rotation is necessary because it limits the lifespan of a password, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. By regularly changing passwords, the window of time during which a stolen password remains valid is condensed, making it more challenging for cybercriminals to exploit compromised credentials. This practice helps protect sensitive information and complies with various security regulations.
The difference between manual and automatic password rotation lies in the process and efficiency:
Rotate passwords for normal accounts every 30, 60 or 90 days. For privileged accounts, rotate more frequently, ideally after each use. This minimizes the risk of credential compromise.
Password rotation enhances compliance by:
This practice, while debated, remains a key component in many security frameworks and audits.

Our Other Identity & Access Management Products