Need Help? We are right here!
Search Results:
×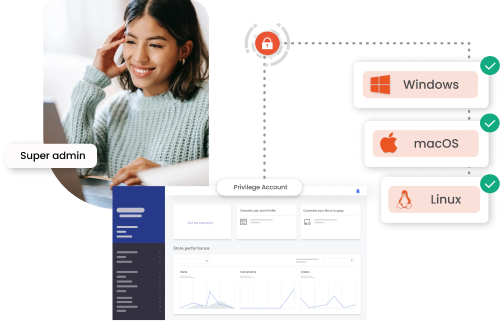
Endpoint Privilege Management (EPM) reduces endpoint risks through the process of least privilege and application control. It ensures that users receive only the required level of access, while unauthorized applications are either restricted or blocked.
By allowing only trusted applications to operate under minimal privileges, EPM Management protects desktops, laptops, and servers from being compromised. The Endpoint Privilege Manager is one of the important features of Privileged Access Management (PAM) and also a foundational tool for strengthening endpoint defenses against attacks exploiting privileged access.







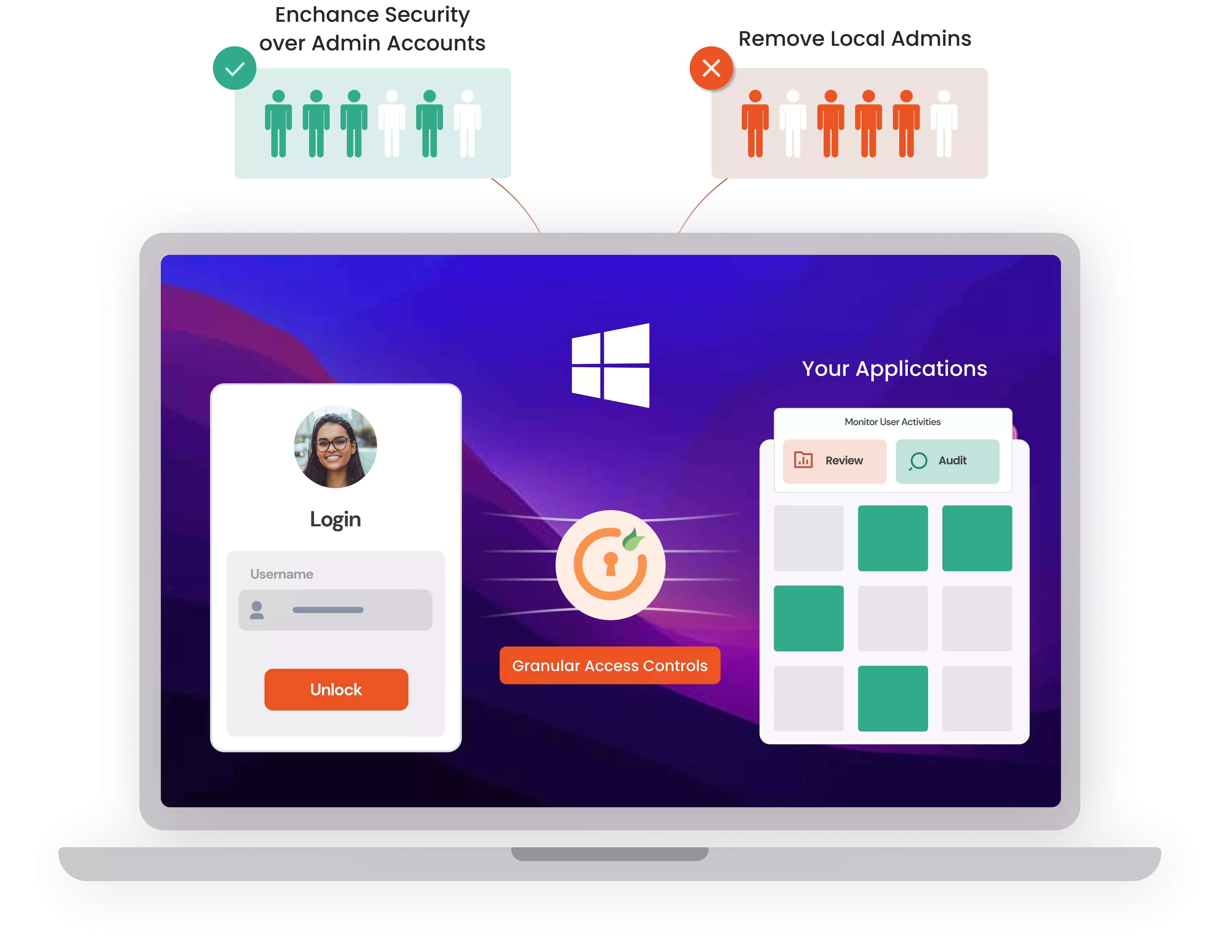
EPM system, specializing in privilege management for Windows and Mac operating systems, removes local admin rights and applies the least privilege principles to both platforms. By fine-tuning access and permissions on Windows and macOS, EPM ensures a balance between security and uninterrupted workflow.
Specifically, the EPM Windows component focuses on:
TThe EPM solution streamlines compliance, controls root access, and enforces the principle of least privilege across Linux environments. This approach enhances cybersecurity frameworks for organizations operating within Linux-based infrastructures.


Endpoint Privilege Management (EPM) improves user experience and IT efficiency by removing local admin rights.
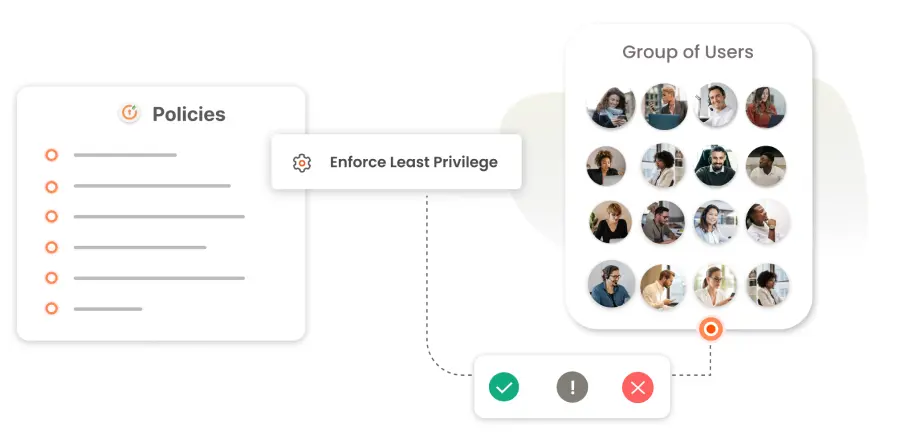
EPM crafts precise, conditional policies for varying user groups, from HR to DevOps, by assessing the context and specifics of applications and operations.
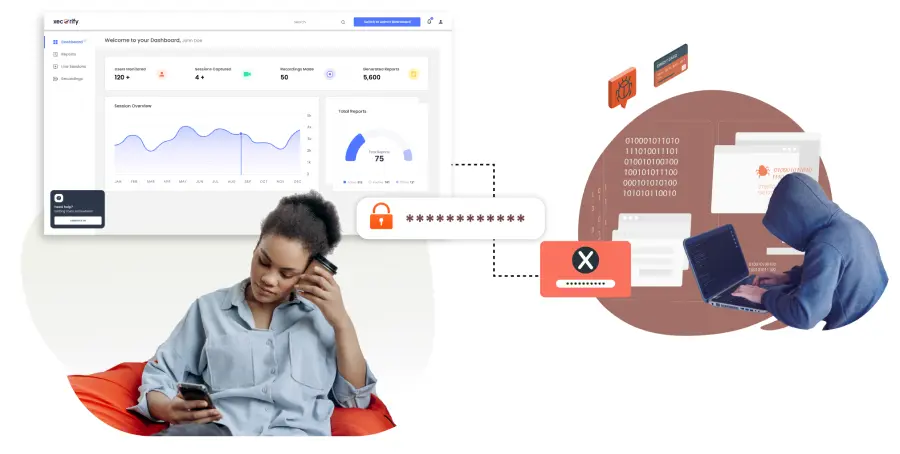
Endpoint Privilege Management (EPM) defends against credential theft and ransomware by securing credentials and their storage, using strategies such as credential lures to block lateral movements by attackers.

The Policy Audit feature allows organizations to track and analyze attempts at privilege elevation, creating audit trails that enhance visibility and control.

Endpoint Privilege Management facilitates the centralized management of zero-trust security controls.
Automatically adjusts user privileges to match their needs within security guidelines, by automatically elevating the privileges when the user's requirements match security protocols.


Advanced Endpoint Security Manager leverages user behavior analysis and intelligence data for early threat detection and risk reduction. These features enable monitoring and managing privileged sessions, strengthening security protocols, and simplifying threat identification and response processes.
It includes features such as:
Through automation, it identifies privileged accounts across endpoints and applications, overcoming the hassle of manual tracking.
EPM solution offers comprehensive endpoint protection with provisioning, role-based authorization, and just-in-time privilege assignment to prevent data breaches and cyberattacks.
Endpoint Privilege Management makes laptops and smartphones safer from hackers. It stops ransomware, keeps data safe, and blocks unauthorized access to networks.
Manual mistakes can compromise security. Endpoint Privilege Management enforces robust password policies, including password management and rotation, and regular device updates to block cyber threats and protect your network.
EPM meets various regulatory requirements, simplifying compliance tracking with detailed privileged action records. This identifies security gaps, automates critical processes, and reduces IT staff workload and errors. Key compliances include PCI-DSS, GDPR, SAMA, and more.
Privileged Access Management seamlessly integrates into your existing infrastructure, ensuring secure and
managed access to critical systems

I can't speak highly enough regarding miniOrange, I am totally satisfied with the process and results in every regard.
5.0

Awesome tech service, Awesome product. Overall Awesome people. This solution is very simple and easy to implement
5.0
Endpoint Privilege Management (EPM) is designed to protect sensitive resources and data from unauthorized access by regulating access rights and administrative privileges on endpoints, such as laptops, smartphones, and servers.
It ensures that only authorized users have the necessary level of access to perform their job functions, effectively safeguarding against unauthorized access and potential cyber threats.
Endpoint management operates by authenticating and supervising the access rights of endpoint devices, like computers and mobile phones, to a network. It involves applying comprehensive security policies to these devices to prevent any external or internal threats resulting from their access to the network.
This process ensures that all devices comply with the organization's security standards before granting them network access, effectively maintaining a secure IT environment.
The three main steps of endpoint security involve:
- Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP): EPP focuses on preventing known threats by using traditional security measures such as antivirus, anti-malware, firewall, and more to secure endpoint devices.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR takes a more dynamic approach by continuously monitoring endpoints for suspicious activities, enabling real-time threat detection, investigation, and response to advanced threats.
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR): XDR expands beyond endpoints to offer a more comprehensive security solution that aggregates and correlates data across various sources—like email, server, cloud, and network—providing a holistic view and response to threats across the entire IT environment.
The difference between Intune and Endpoint Manager lies in their scope and functionality. Intune is a cloud-based service focused on mobile device management (MDM) and mobile application management (MAM), enabling organizations to manage devices and applications securely from anywhere.
On the other hand, Microsoft Endpoint Manager is a more comprehensive platform that unifies and simplifies access and management of both Intune and System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM), along with other components like Endpoint Analytics and Windows Autopilot. Essentially, Endpoint Manager serves as a centralized hub for managing and securing devices across your organization, incorporating the functionalities of Intune, SCCM, and more.
The difference between Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) and endpoint management lies in their primary functions and objectives. Endpoint management encompasses the overall processes and technologies used to authenticate, supervise, and enforce security policies on endpoint devices to prevent unauthorized access and threats. It aims at ensuring the health, compliance, and security of devices across a network.
On the other hand, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is specifically designed to detect, investigate, and respond to cybersecurity threats and incidents that have bypassed traditional security measures, such as Endpoint Protection Platforms (EPP) or other security defenses. EDR solutions provide real-time monitoring and analysis to identify suspicious activities and offer tools for incident response and investigation, thereby enhancing an organization's ability to quickly mitigate and recover from security breaches.

Our Other Identity & Access Management Products