Need Help? We are right here!
Search Results:
×






Secure Remote Access is a vital IT security strategy that enables authorized personnel to assist employees with tech issues. It allows employees to log into secure company devices while working remotely and monitor usage. To protect sensitive data, it’s essential to implement robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access. At miniOrange, we combine various technologies and strategies to offer secure Remote Access Solutions that grant different access levels based on roles and responsibilities. This approach safeguards systems and applications while ensuring their operational efficiency, making it essential for any organization to prioritize cybersecurity in a remote work environment.
VPNs are the most widely used method for remote access, utilizing authentication and encryption to create a secure connection to a private network via the Internet.
IPsec, SSL VPNs, and SSH are key technologies for securing remote access. SSL VPNs use authentication and encryption for secure browser-based connections, allowing remote users to safely access organizational resources.
SSH enables secure connections to remote computers without passwords, offering text-mode terminal access to systems running an SSH server.
IPsec establishes encrypted connections, like VPNs, over public networks to ensure data confidentiality and integrity.
SSO allows users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials, reducing password fatigue and minimizing security risks. By centralizing authentication, it enables consistent security policies across applications.
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring two or more verification factors before granting access. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access since attackers need more than just a password.
PAM manages and monitors access for users with elevated privileges, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive systems. It enforces policies on how and when privileged accounts can be used and includes session monitoring for enhanced security.
Authenticate users or entities through the organization's identity and authentication system before initiating a remote access session.
Define who can access which systems, when, from which devices, and what specific actions they can perform.
Upon successful authentication, grant users controlled access based on least privilege or role-based access control (RBAC) principles.
Establish remote sessions (RDP, SSH, SQL, or VNC) through encrypted pathways, ensuring no need for additional credentials during the session.
Record all sessions for review, monitor them in real-time for suspicious activities, and send audit logs to SIEM systems for better security insights.
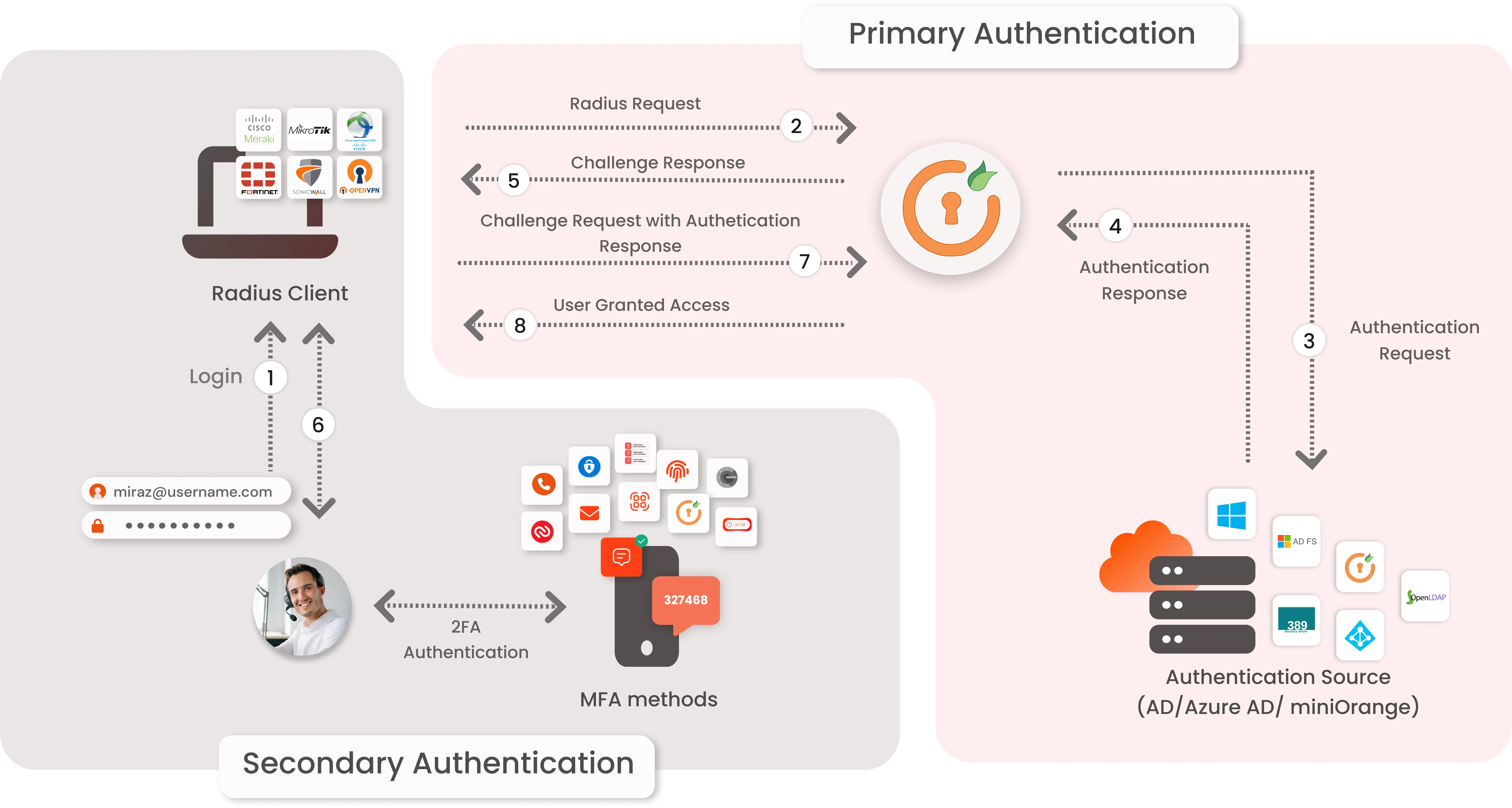
Identity solutions from miniOrange can be easily deployed in your organization's existing environment.
Securing remote access allows users to connect to geographically dispersed assets through a unified system, simplifying access management effectively.

GAC Implementing secure remote access enables precise permissions for third parties, ensuring users access only the resources necessary for their roles.
Secure remote access streamlines operations, allowing employees to work from anywhere, increasing efficiency, and simplifying administrative management for IT teams.
Secure remote access strengthens control over user access, helping enforce policies, maintain compliance, and ensure organizational security standards are met.
Secure remote access solutions assist organizations in meeting compliance standards by providing necessary controls, documentation, and protection for sensitive data.
"Nahdi wanted to adopt SSO, and they were using Siebel CRM, but it didn’t support any SSO protocols. Changing the entire CRM system and transferring data from one CRM to another is a time-consuming job…"
Read customer storiesEnterprises can ensure secure remote access through a Zero Trust strategy by verifying the identity of every user and device, enforcing least privilege access, using multi-factor authentication, continuously monitoring activity, and encrypting all communications across the network.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is a secure remote access model that enables access to private applications on the network only after proper verification. Unlike traditional approaches, ZTNA does not automatically trust users; instead, it grants access based on roles, least privilege, and other granular security controls, ensuring that users receive only the necessary permissions while minimizing security risks.
It provides application-specific access rather than full network access like VPNs. It continuously verifies user identity and device security, enforces least privilege, and applies granular security controls, reducing the attack surface and limiting potential threats.
Identity, Access, and Beyond
